Question: A microscope takes light rays from a point on a microscopic object, very near the optic axis, and transforms them into parallel light rays that
A microscope takes light rays from a point on a microscopic object, very near the optic axis, and transforms them into parallel light rays that will be focused by a human eye’s lens onto the eye’s retina (Fig. 7.8). Use matrix methods to explore the operation of such a microscope. A single lens (magnifying glass) could do the same job (rays from a point converted to parallel rays). Why does a microscope need two lenses? What focal lengths and lens separations are appropriate for the eye to resolve a bacterium 100 μm in size?
Fig. 7.8.
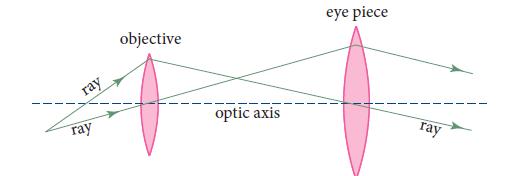
ray ray objective optic axis eye piece ray
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
ANSWER A microscope uses two lenses to magnify an object because each lens has a limit to its magnification power The first lens called the objective ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


