Question: A Sagnac interferometer is a rudimentary version of a laser gyroscope for measuring rotation with respect to an inertial frame. The optical configuration is shown
A Sagnac interferometer is a rudimentary version of a laser gyroscope for measuring rotation with respect to an inertial frame. The optical configuration is shown in Fig. 9.12. Light from a laser L is split by a beam splitter B and travels both clockwise and counterclockwise around the optical circuit, reflecting off three plane mirrors. The light is then recombined at B, and interference fringes are viewed through the telescope T . The whole assembly rotates with angular velocity Ω. Calculate the difference in the time it takes light to traverse the circuit in the two directions, and show that the consequent fringe shift (total number of fringes that enter the telescope during one round trip of the light in the interferometer) can be expressed as △N = 4AΩ/(cλ), where λ is the wavelength, and A is the area bounded by the beams. Show further that, for a square Sagnac interferometer with side length L, the rate at which fringes enter the telescope is ΩL/λ.
Fig. 9.12
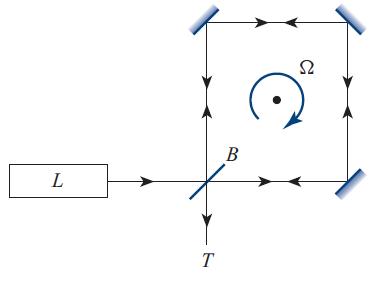
L T
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The difference in the time it takes light to traverse the circuit in the two directions can be calcu... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


