Question: Consider the triangle formed by the three geodesics in Fig. 28.3. In a flat space, the exterior angle must equal + . However,
Consider the triangle formed by the three geodesics in Fig. 28.3. In a flat space, the exterior angle ζ must equal θ + ψ. However, if the space is homogeneous and positively curved, then the angle deficit △ ≡ θ + ψ − ζ will be positive.
(a) By considering the geometry of the 2-dimensional surface of a sphere embedded in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, show that the area of the triangle is △/K.
(b) Make a conjecture (or, better still, devise a demonstration) as to the formula for the area of a triangle in a negatively curved homogeneous space.
These results are special cases of the famous Gauss-Bonnet theorem, which allows for the possibility that the topology of the space might not be simple.
Figure 28.3.
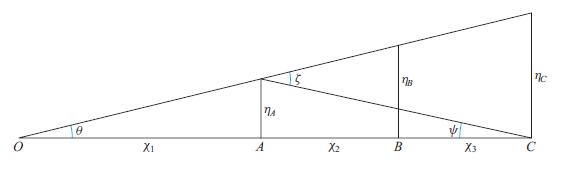
0 X1 MA A X MB B X3 nc
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve this question lets consider each part separately a To show that the area of the triangle is K in a positively curved space we can use the geo... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


