Question: Derive the evolution equations (10.48) for three-wave mixing. You could proceed as follows. (a) Insert expressions (10.27) and (10.28) into the general wave equation (10.30)
Derive the evolution equations (10.48) for three-wave mixing. You could proceed as follows.
(a) Insert expressions (10.27) and (10.28) into the general wave equation (10.30) and extract the portions with frequency ω3 = ω1 + ω2, thereby obtaining the generalization of Eq. (10.33):
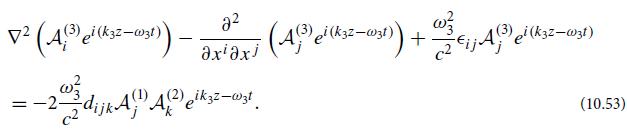
(b) Explain why ei(k3 · x−ω3t)f(3) satisfies the homogeneous wave equation (10.50). Then, splitting each wave into its scalar field and polarization vector, Ai(n) ≡ A(n)fi(n), and letting each A(n) be a function of z (because of the boundary condition that the three-wave mixing begins at the crystal face z = 0), show that Eq. (10.53) reduces to
![]()
where α3 is a constant of order unity that depends on the relative orientations of the unit vectors ez, f(3), and K̂3. Note that, aside from α3, this is the same evolution equation as for our idealized isotropic, dispersion-free medium, Eq. (10.34a). Show that, similarly, A(1)(z) and A(2)(z) satisfy the same equations (10.34b) and (10.34c) as in the idealized case, aside from multiplicative constants α1 and α2.
(c) Adopting the renormalizations
![]()
with ζn so chosen that the photon-number flux for wave n is proportional to ![]()
show that your evolution equations for An become Eqs. (10.48), except that the factor β' and thence the value of κ might be different for each equation.
(d) Since the evolution entails one photon with frequency ω1 and one with frequency ω2 annihilating to produce a photon with frequency ω3, it must be that
![]()
(These are called Manley-Rowe relations.) By imposing this on your evolution equations in part (c), deduce that all three coupling constants κ must be the same, and thence also that all three β' must be the same; therefore the evolution equations take precisely the claimed form, Eqs. (10.48).
Equations
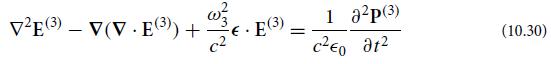
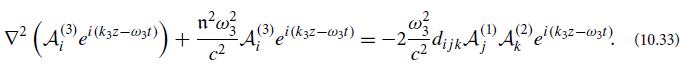
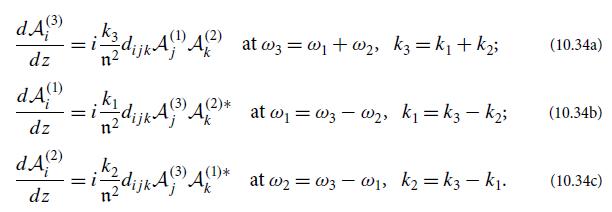
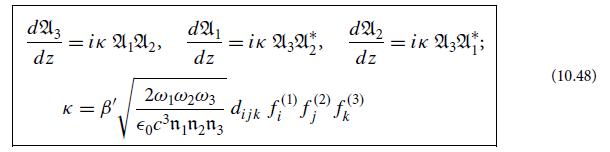
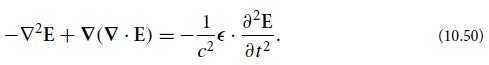
2 (A() ei k32-(31)) D - 2 xx/ (4() el (ksz-wist)). -2 dijk AD A() eikzz-wzt + A 2 A ei (k3z-w3t) (10.53)
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To derive the evolution equations for threewave mixing lets break it down into the individual parts as indicated in the steps a Generalization of Eq 1... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


