Question: Suppose that a spherical bubble has just been created in the water above the hydrofoil in the previous exercise. Here we analyze its collapsethe decrease
Suppose that a spherical bubble has just been created in the water above the hydrofoil in the previous exercise. Here we analyze its collapse—the decrease of the bubble’s radius R(t) from its value Ro at creation, using the incompressible approximation (which is rather good in this situation). This analysis is an exercise in solving the Euler equation.
(a) Introduce spherical polar coordinates with origin at the center of the bubble, so the collapse entails only radial fluid motion, v = v(r , t)er. Show that the incompressibility approximation ∇ · v = 0 implies that the radial velocity can be written in the form v = w(t)/r2. Then use the radial component of the Euler equation (13.44) to show that
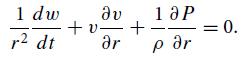
At fixed time t, integrate this outward from the bubble surface at radius R(t) to a large enough radius that the bubble’s influence is no longer felt. Thereby obtain
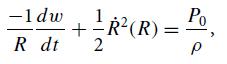
where P0 is the ambient pressure and − Ṙ(R) is the speed of collapse of the bubble’s surface when its radius is R. Assuming vanishing collapse speed when the bubble is created, Ṙ(Ro) = 0, show that
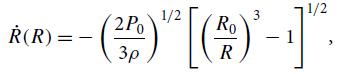
which can be integrated to get R(t).
(b) Suppose that bubbles formed near the pressure minimum on the surface of the hydrofoil are swept back onto a part of the surface where the pressure is much larger. By what factor Ro/R must the bubbles collapse if they are to create stresses that inflict damage on the hydrofoil?
Pistol shrimp can create collapsing bubbles and use the shock waves to stun their prey. A modification of this solution is important in interpreting the fascinating phenomenon of sonoluminescence (Brenner, Hilgenfeldt, and Lohse, 2002), which arises when fluids are subjected to high-frequency acoustic waves that create oscillating bubbles. The temperatures inside these bubbles can get so large that the air becomes ionized and radiates.
Equation 13.44.
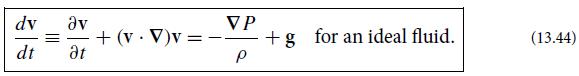
1 dw r2 dt tv- + ar 1 = 0.
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve this problem lets analyze the given information step by step a We start by considering the incompressible fluid flow in spherical polar coord... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


