Question: Solve the differential equation obtained in Example 8.4 to determine the amount x(t) of salt in the tank at time t minutes. Initially the tank
Solve the differential equation
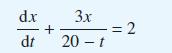
obtained in Example 8.4 to determine the amount x(t) of salt in the tank at time t minutes. Initially the tank contains pure water.
Data from Example 8.4
Suppose that a tank initially contains 80 litres of pure water. At a given instant (taken to be t = 0) a salt solution containing 0.25 kg of salt per litre flows into the tank at a rate of 8 litres min–1. The liquid in the tank is kept homogeneous by constant stirring. Also, at time t = 0 liquid is allowed to flow out from the tank at a rate of 12 litres min–1. Show that the amount of salt x(t) (in kg) in the tank at time t (min) ≥ 0 is determined by the mathematical model
![]()
dx dt + 3x 20 - t = 2 ||
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We find that the appropriate initial condition is x0 0 Hence we have the dif... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


