Question: Chebyshevs inequality, introduced in Chapter 3 Exercise 45, is valid for continuous as well as discrete distributions. It states that for any number k
Chebyshev’s inequality, introduced in Chapter 3 Exercise 45, is valid for continuous as well as discrete distributions. It states that for any number k ≥ 1, P(lX – μl ≥kσ) ≤ 1/k2 (see the aforementioned exercise for an interpretation and Chapter 3 Exercise 163 for a proof). Obtain this probability in the case of a normal distribution for k = 1, 2, and 3, and compare to the Chebyshev upper bound.
Data From Chapter 3 Exercise 45

Data From Exercise 163 in Chapter 3
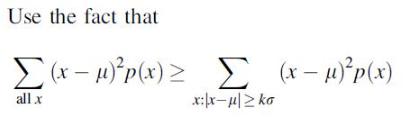
A result called Chebyshev's inequality states that for any probability distribution of a rv X and any number k that is at least 1, P(|X-u ko) 1/k. In words, the probability that the value of X lies at least k standard deviations from its mean is at most 1/k.
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Chebyshevs inequality provides a way to estimate the probability that a random variable falls a certain number of standard deviations away from its me... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


