Question: We are given a graph as a set of vertices in V = f{, . . . , n}, with an edge joining any pair
We are given a graph as a set of vertices in V = f{, . . . , n}, with an edge joining any pair of vertices in a set ![]() We assume that the graph is undirected (without arrows), meaning that (i, j) ∈ E implies (j, i) ∈ E. As in Section 4.1, we define the Laplacian matrix by
We assume that the graph is undirected (without arrows), meaning that (i, j) ∈ E implies (j, i) ∈ E. As in Section 4.1, we define the Laplacian matrix by
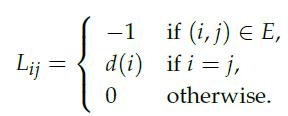
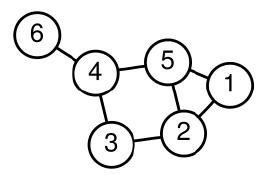
Here, d(i) is the number of edges adjacent to vertex i. For example, d(4) = 3 and d(6) = 1 for the graph in Figure 4.4.
1. Form the Laplacian for the graph shown in Figure 4.4.
2. Turning to a generic graph, show that the Laplacian L is symmetric.
3. Show that L is positive-semidefinite, proving the following identity, valid for any u ∈ Rn: Find the values![]() for two unit vectors ek, el such that (k, l) ∈ E.
for two unit vectors ek, el such that (k, l) ∈ E.
4. Show that 0 is always an eigenvalue of L, and exhibit an eigenvector.
5. The graph is said to be connected if there is a path joining any pair of vertices. Show that if the graph is connected, then the zero eigenvalue is simple, that is, the dimension of the null space of L is 1.Prove that if uTLu = 0, then ui = uj for every pair (i, j) ∈ E.
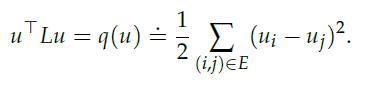
EC V X V. x
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 The Laplacian for the graph is 2 L is symmetric by definition of ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


