Question: (a) In Figure (22.19 b), is the electroscope as a whole positively charged, negatively charged, or neutral? (b) How does the magnitude of the positive
(a) In Figure \(22.19 b\), is the electroscope as a whole positively charged, negatively charged, or neutral?
(b) How does the magnitude of the positive charge on the electroscope ball compare with the magnitude of the negative charge on the leaves?
(c) Is the force exerted by the rod on the electroscope ball attractive or repulsive? Is the force exerted by the rod on the leaves attractive or repulsive?
(d) How do you expect the magnitude of the force the rod exerts on the ball to compare with the magnitude of the force the rod exerts on the leaves?
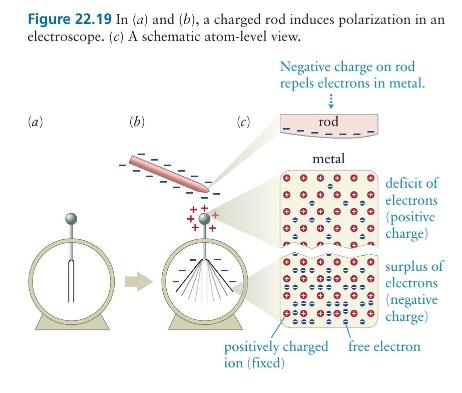
Figure 22.19 In (a) and (b), a charged rod induces polarization in an electroscope. (c) A schematic atom-level view. (a) (b) (c) Negative charge on rod repels electrons in metal. rod metal deficit of electrons (positive charge) surplus of electrons (negative 0 0 0 0 0 charge) positively charged free electron ion (fixed)
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Before the charged rod is brought nearby the electroscope is neutral meaning it has as many positi... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


