Question: Aromatic molecules such as benzene typically undergo substitution when reacted with an electrophile such as Br 2 , whereas alkenes such as cyclohexene most commonly
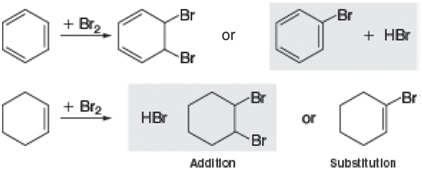
What is the reason for the change in preferred reaction in moving from the alkene to the arene? Use the Hartree€“ Fock 6-31G* model to obtain equilibrium geometries and energies for reactants and products of both addition and substitution reactions of both cyclohexene and benzene (four reactions in total). Assume trans addition products (1,2-dibromocyclohexane and 5,6-dibromo-1,3-cyclohexadiene). Use your calculated energies for the reactants and products to determine the change in energy in all four reactions. Is your result consistent with what is actually observed? Are all four reactions exothermic? If one or more are not exothermic, provide a rationale as to why.
Br Br + Br, + HBr or Br Br Br + Br2 HBr or Br Addition Substitutlon
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Bromination of benzene bromination of cyclohexene Both addition of bromine to cyclohexene 1... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


