Certain solid substances, known as hydrated compounds, have well-defined molecular ratios of water to some other species.
Question:
Certain solid substances, known as hydrated compounds, have well-defined molecular ratios of water to some other species. For example, calcium sulfate dihydrate (commonly known as gypsum, (CaSO4•2H2O), has 2 moles of water per mole of calcium sulfate; alternatively, it may be said that 1 mole of gypsum consists of 1 mole of calcium sulfate and 2 moles of water. The water in such substances is called water of hydration.
In order to eliminate the discharge of sulfuric acid into the environment, a process has been developed in which the acid is reacted with aragonite (CaCO3) to produce calcium sulfate. The calcium sulfate then comes out of solution in a crystallizer to form a slurry (a suspension of solid particles in a liquid) of solid gypsum particles suspended in an aqueous CaSO4 solution. The slurry flows from the crystallizer to a filter in which the particles are collected as a filter cake. The filter cake, which is 95.0 wt% solid gypsum and the remainder CaSO4 solution, is fed to a dryer in which all water (including the water of hydration in the crystals) is driven off to yield anhydrous (water-free) CaSO4 as product. A flowchart and relevant process data are given below.
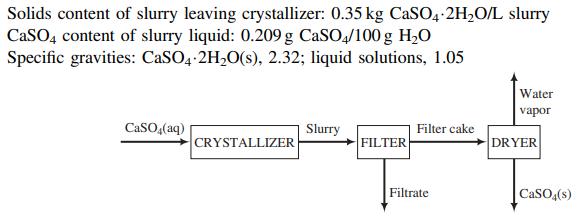
(a) Briefly explain in your own words the functions of the three units (crystallizer, filter, and dryer).
(b) Take a basis of one liter of solution leaving the crystallizer and calculate the mass (kg) and volume (L) of solid gypsum, the mass of CaSO4 in the gypsum, and the mass of CaSO4 in the liquid solution.
(c) Calculate the percentage recovery of CaSO4—that is, the percentage of the total CaSO4 (precipitated plus dissolved) leaving the crystallizer recovered as solid anhydrous CaSO4.
(d) List five potential negative consequences of discharging H2SO4 into the river passing the plant.
Step by Step Answer:

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 978-1119498759
4th edition
Authors: Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard




