Question: Write a function to delete an element from a given position in the sparse matrix representation of Section 12.2. 12.2 Matrix Representations Some applications must
Write a function to delete an element from a given position in the sparse matrix representation of Section 12.2.
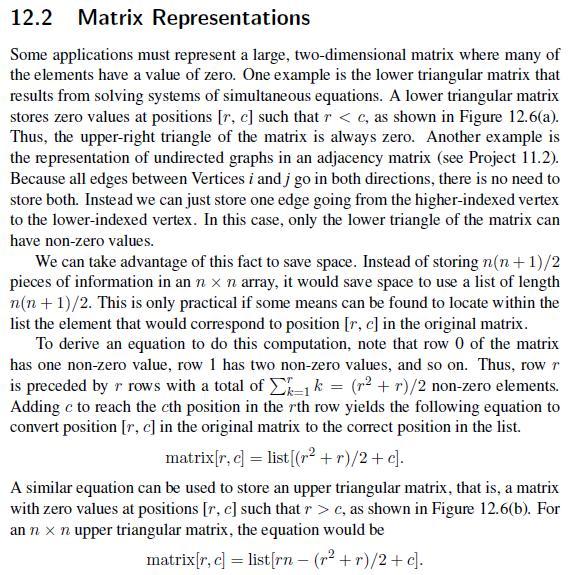
12.2 Matrix Representations Some applications must represent a large, two-dimensional matrix where many of the elements have a value of zero. One example is the lower triangular matrix that results from solving systems of simultaneous equations. A lower triangular matrix stores zero values at positions [r, c] such that r < c, as shown in Figure 12.6(a). Thus, the upper-right triangle of the matrix is always zero. Another example is the representation of undirected graphs in an adjacency matrix (see Project 11.2). Because all edges between Vertices i and j go in both directions, there is no need to store both. Instead we can just store one edge going from the higher-indexed vertex to the lower-indexed vertex. In this case, only the lower triangle of the matrix can have non-zero values. We can take advantage of this fact to save space. Instead of storing n(n+1)/2 pieces of information in an n x n array, it would save space to use a list of length n(n+1)/2. This is only practical if some means can be found to locate within the list the element that would correspond to position [r, c] in the original matrix. To derive an equation to do this computation, note that row 0 of the matrix has one non-zero value, row 1 has two non-zero values, and so on. Thus, row r is preceded by r rows with a total of 1k = (r + r)/2 non-zero elements. Adding c to reach the cth position in the rth row yields the following equation to convert position [r, c] in the original matrix to the correct position in the list. matrix[r, c] = list [(r +r)/2+c]. A similar equation can be used to store an upper triangular matrix, that is, a matrix with zero values at positions [r, c] such that r>c, as shown in Figure 12.6(b). For an n x n upper triangular matrix, the equation would be matrix[r, c] = list[rn - (r +r)/2+c].
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The image you provided explains how a lower or upper triangular matrix can be represented in a condensed form to save space when coding This form of s... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


