Question: If a variable force of magnitude F(x) moves an object of mass m along the x-axis from x 1 to x 2 , the objects
If a variable force of magnitude F(x) moves an object of mass m along the x-axis from x1 to x2, the object’s velocity y can be written as dx/dt (where t represents time). Use Newton’s second law of motion F = m(dy/dt) and the Chain Rule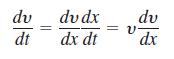
to show that the net work done by the force in moving the object from x1 to x2 is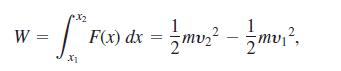
where ν1 and ν2 are the object’s velocities at x1 and x2. In physics, the expression (1/2)mν2 is called the kinetic energy of an object of mass m moving with velocity ν. Therefore, the work done by the force equals the change in the object’s kinetic energy, and we can find the work by calculating this change.
du dt dv dx dx dt - U du dx
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Starting with Newtons second law F mdydt we can rewrite it as dydt Fxm Now we ca... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


