Question: The equation ax 2 + 2x - 1 = 0, where a is a constant, has two roots if a > -1 and a
The equation ax2 + 2x - 1 = 0, where a is a constant, has two roots if a > -1 and a ≠ 0, one positive and one negative: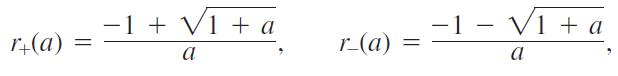
a. What happens to r+(a) as a→ 0? As a→ -1+?
b. What happens to r-(a) as a→ 0? As a→ -1+?
c. Support your conclusions by graphing r+(a) and r-(a) as functions of a. Describe what you see.
d. For added support, graph ƒ(x) = ax2 + 2x - 1 simultaneously for a = 1, 0.5, 0.2, 0.1, and 0.05.
a D + IA - I- = (1)-1 a D + IA + I- = r+(a)
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a To find what happens to ra as a approaches 0 and as a approaches 1 from the right we can use limit... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


