Question: The function (x) = |x| has an absolute minimum value at x = 0 even though is not differentiable at x = 0. Is
The function ƒ(x) = |x| has an absolute minimum value at x = 0 even though ƒ is not differentiable at x = 0. Is this consistent with Theorem 2? Give reasons for your answer.
Theorem 2
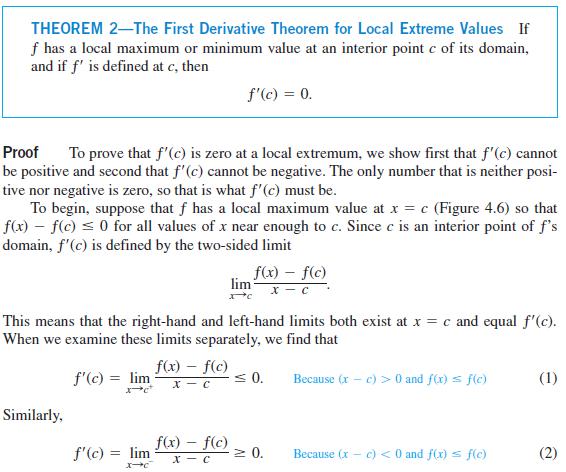
THEOREM 2-The First Derivative Theorem for Local Extreme Values If f has a local maximum or minimum value at an interior point c of its domain, and if f' is defined at c, then Proof To prove that f'(c) is zero at a local extremum, we show first that f'(c) cannot be positive and second that f'(c) cannot be negative. The only number that is neither posi- tive nor negative is zero, so that is what f'(c) must be. To begin, suppose that f has a local maximum value at x = c (Figure 4.6) so that f(x) = f(c) 0 for all values of x near enough to c. Since c is an interior point of f's domain, f'(c) is defined by the two-sided limit Similarly, f'(c) = lim This means that the right-hand and left-hand limits both exist at x = c and equal f'(c). When we examine these limits separately, we find that Because (x-c) > 0 and f(x) = f(c) f'(c) = lim X-C f'(c) = 0. f(x) = f(c) x c f(x) = f(c) - x-c f(x) = f(c) x - C lim 0. 0. Because (x c) < 0 and f(x) = f(c) (1) (2)
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
ANSWER The given function x x has an absolute minimum value at x 0 even though it is not differentia... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


