Question: 3.7.5 Computer Challenge. Consider the partial sums: where 1; 2; : : : are independent and identically distributed as and Can you find an explicit
3.7.5 Computer Challenge. Consider the partial sums:
![]() where 1; 2; : : : are independent and identically distributed as
where 1; 2; : : : are independent and identically distributed as
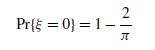
and
![]()
Can you find an explicit formula for the mean time vk for the partial sums starting from S0 D k to exit the interval [0;N] D f0;1; : : : ;Ng? In another context, the answer was found by computing it in a variety of special cases.
Note: A simple random walk on the integer plane moves according to the rule:
If .Xn;Yn/ D .i; j/, then the next position is equally likely to be any of the four points .iC1; j/; .i????1; j/; .i; jC1/, or .i; j????1/. Let us suppose that the process starts at the point .X0;Y0/ D .k; k/ on the diagonal, and we observe the process only when it visits the diagonal. Formally, we define
1 D minfn > 0IXn D Yng;
and m D minfn > m????1IXn D Yng:
It is not hard to show that S0 D k; Sm D Xm D Ym; m > 0;
is a version of the above partial sum process.
Sok and Sm=k+$1++m, k> 0,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


