Question: 7.5. Computer Challenge. Consider the partial sums: Can you find an explicit formula for the mean time Vk for the partial sums starting from So
7.5. Computer Challenge. Consider the partial sums:
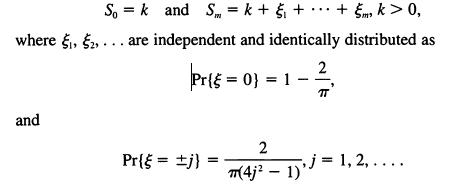
Can you find an explicit formula for the mean time Vk for the partial sums starting from So = k to exit the interval [0, N] = {0, 1, . . . , N}? In another context, the answer was found by computing it in a variety of special cases.
(Note: A simple random walk in the integer plane moves according to the rule, If (X,,, (i, j), then the next position is equally likely to be any of the four points (i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), or (i, j - 1). Let us suppose that the process starts at the point (X0, Yo) = (k, k) on the diagonal, and we observe the process only when it visits the diagonal. Formally, we define T,=min{n> 0; X,, and T = min{n > T,,,-.; X,, = It is not hard to show that So = k, S,,, = XT., = YT,., m > 0, is a version of the above partial sum process.
Sok and S = k + + + m k > 0, where 1, 2, ... are independent and identically distributed as Pr{0} = 1 2 T and 2 Pr{ = j} m(4j 1)' j = 1, 2,....
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


