Question: Consider the two-unit system with parallel redundancy discussed in example 9.6 on condition that the lifetimes of the units are exponential with parameters (lambda_{1}) and
Consider the two-unit system with parallel redundancy discussed in example 9.6 on condition that the lifetimes of the units are exponential with parameters \(\lambda_{1}\) and \(\lambda_{2}\), respectively. The other model assumptions listed in example 9.6 remain valid.
Model the behavior of the system by a Markov chain and draw the transition graph.
Data from Example 9.6
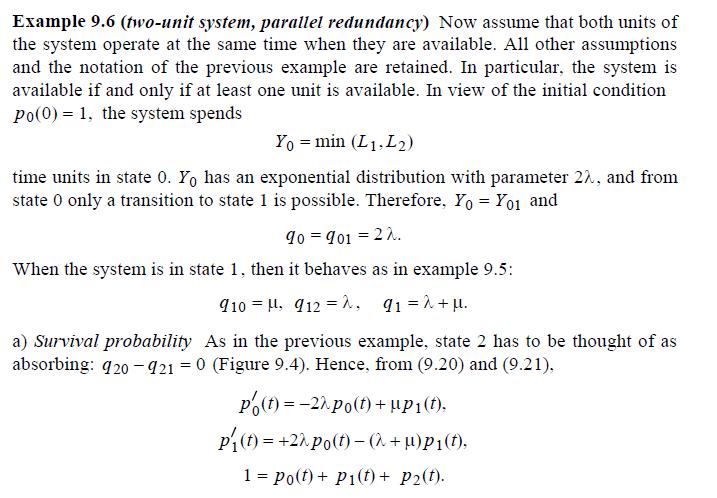
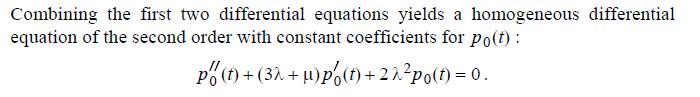
Example 9.6 (two-unit system, parallel redundancy) Now assume that both units of the system operate at the same time when they are available. All other assumptions and the notation of the previous example are retained. In particular, the system is available if and only if at least one unit is available. In view of the initial condition Po(0) = 1, the system spends Yo min (L1,L2) time units in state 0. Yo has an exponential distribution with parameter 2%, and from state 0 only a transition to state 1 is possible. Therefore, Yo = Y01 and 90=901 = 27. When the system is in state 1, then it behaves as in example 9.5: 910, 912, 91=2+. a) Survival probability As in the previous example, state 2 has to be thought of as absorbing: 920-921 = 0 (Figure 9.4). Hence, from (9.20) and (9.21), Po(t)=-2 po(t)+"p(t). == P(t) = +22 po(t)-(+l)pi(t), 1 Po(t)+ P1(t)+ P2(t).
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


