Question: S Non-parametric analysis of variance. Let G D 1; : : : ; s and B D ik W i 2 G; 1 k ni
S Non-parametric analysis of variance. Let G D ¹1; : : : ; sº and B D ¹ik W i 2 G;
1 k ni º for certain ni 2. Also, let n D jBj and X D .Xik/ik2B be a vector of independent real-valued observations Xik with unknown continuous distributions Qi . Furthermore, let Rik be the rank of Xik in X and R D .Rik/ik2B. Test the null hypothesis H0 W Q1 D D Qs DW Q against the alternative H1 W Qi Qj for a pair .i; j / 2 G2 by applying the F -test from Example (12.33) to R instead of X. With this in mind, verify the following:
(a) M.R/ D .nC1/=2 and V
tot.R/ D n.nC1/=12.
(b) The F -statistic V
bg.R/=V
wg.R/ is an increasing function of the Kruskal–Wallis test statistic
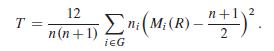
(c) In the case s D 2, T is given by
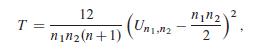
where Un1;n2 is the U-statistic from Lemma (11.24). Hence, a Kruskal–Wallis test with rejection region ¹T > cº of H0 against H1 is equivalent to a two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test.
(d) Under the null hypothesis H0, T has the expectation E.T / D s1, and the distribution of T does not depend on Q. Hint: Recall the proofs of Theorems (11.25) and (11.28).
(e) Convince yourself that T !d 2 s1 under H0, in the limit as ni !1for all i 2 G.
T 12 n(n+1) n 2 n (Mi (R)- "+1). iG ni 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


