Question: A batch reactor converts component A into B, which in turn decomposes into C: where k 1 = k 10 e -E 1 RT and
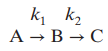 where k1 = k10e-E1 ˆ•RT and k2 = k20e-E2 ˆ•RT.
where k1 = k10e-E1 ˆ•RT and k2 = k20e-E2 ˆ•RT.
The concentrations of A and B are denoted by x1 and x2, respectively. The reactor model is
dx1 / dt = k10x1e-E1 /RT
dx2 / dt = k10x1e-E1 /RT - k20x2e-E2 /RT
Thus, the ultimate values of x1 and x2 depend on the reactor temperature as a function of time. For
k10 = 1.335 × 1010 min-1, k20 = 1.149 × 1017 min-1
E1 = 75,000 Jˆ•g mol, E2 = 125,000 Jˆ•g mol
R = 8.31 Jˆ•(g mol K) x10 = 0.7 molˆ•L, x20 = 0
Find the constant temperature that maximizes the amount of B, for 0 ‰¤ t ‰¤ 6 min.
k, k, A B C
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The reactor equations are Where k 1 133510 10 e 75000 831T k 2 114910 17 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (2 attachments)
1602_606321ef1ba81_683267.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
1602_606321ef1ba81_683267.docx
120 KBs Word File


