Question: Consider the block diagram in Fig. E24.2 of the multiple feedback loops involved in the Central Dogma schematic from Fig. 24.3, namely, genetic regulation C
(i) Derive the transfer function from the external input (u) to the output (y) for each of the three cases shown in Fig. E24.2 (a), (b), and (c)
(ii) Assume that the feedback mechanisms operate via proportional control with corresponding controller gains Kci. Derive the closed-loop transfer function from the external input u to the output y in block diagram (b).
(iii) Consider a simplified biological circuit in which only genetic regulation is active (C1). Derive the closed-loop transfer function and comment on the key differences between this transfer function and the one from part (b).
(iv) Give several reasons why the natural feedback architecture with all three controllers operating is more effective than the control architecture in part (c).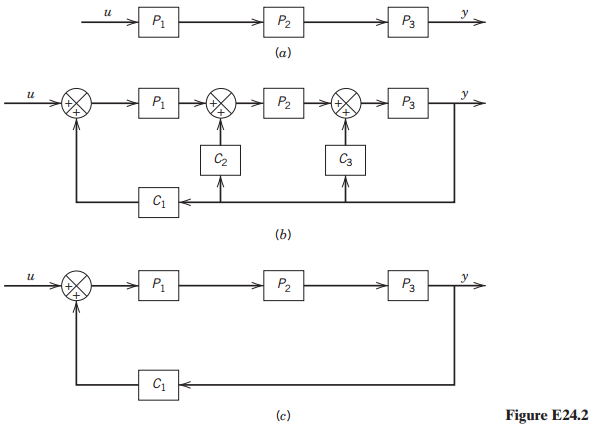
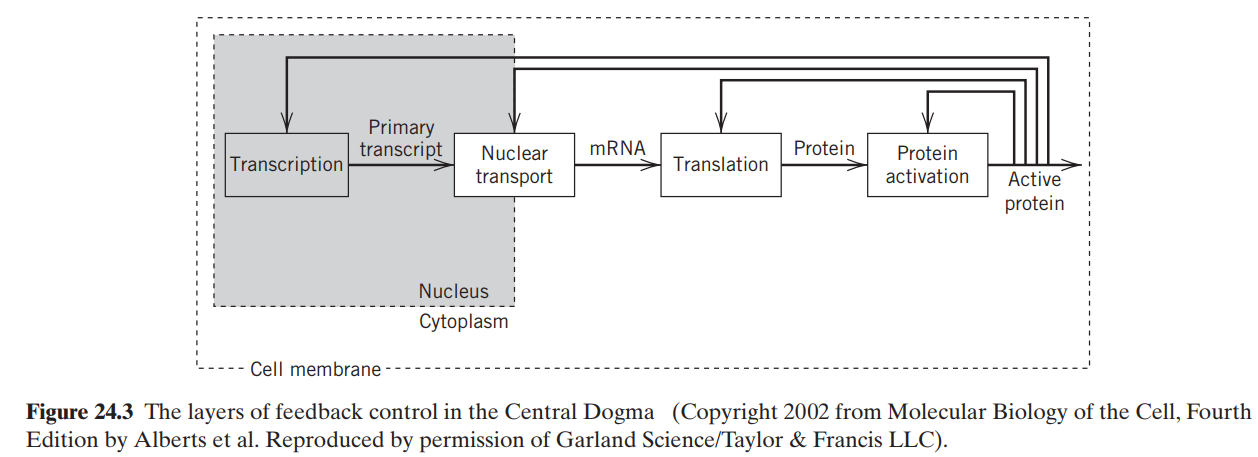
P1 P2 P3 (a) P1 P2 P3 C2 C3 C1 (b) P1 P2 P3 C1 Figure E24.2 (c) Primary transcript Protein Nuclear transport MRNA Transcription Translation Protein activation Active protein Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Figure 24.3 The layers of feedback control in the Central Dogma (Copyright 2002 from Molecular Biology of the Cell, Fourth Edition by Alberts et al. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis LLC).
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (183 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
ia y P 1 P 2 P 3 u ib Algebra here follows y P 3 C 3 y P 2 C 2 y P 1 u C 1 y P 3 C 3 y P 3 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


