Question: In Example 6.9 we described a common error in Pascal programs caused by the fact that and and or have precedence comparable to that of
In Example 6.9 we described a common error in Pascal programs caused by the fact that and and or have precedence comparable to that of the arithmetic operators. Show how a similar problem can arise in the stream-based I/O of C++ (described in Section C 8.7.3). (Consider the precedence of << and >>, and the operators that appear below them in the C column of Figure 6.1.)
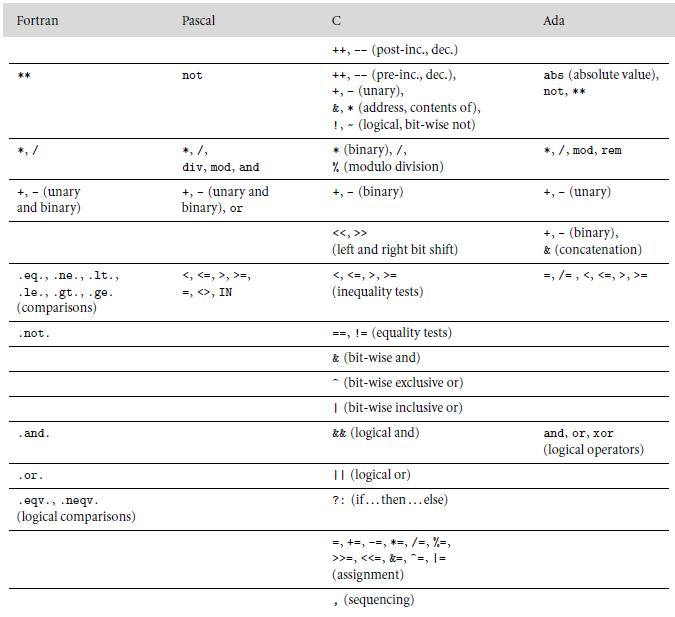
Fortran Pascal Ada ++, -- (post-inc., dec.) abs (absolute value), ++, -- (pre-inc., dec.), +, - (unary), &, * (address, contents of), !, - (logical, bit-wise not) * (binary), /, % (modulo division) not not, ** *, /, 7, mod, rem div, mod, and +, - (unary and binary) +, - (unary and binary), or +, - (binary) +, - (unary) -(bnary), & (concatenation) ,>> (left and right bit shift) =, /= , = .eq., .ne., .lt., .le., gt., - ge. (comparisons) , , >=, ,=, >, >= =, , IN (inequality tests) ==, != (equality tests) .not. & (bit-wise and) * (bit-wise exclusive or) | (bit-wise inclusive or) . and. &k (logical and) and, or, xor (logical operators) II (logical or) ?: (if... then...else) .or. .eqv., .neqv. (logical comparisons) =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %-, >>=,
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
If we write cout 1234 5678 the compil... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


