Question: Your solution to the previous exercise probably doesnt generalize to languages with nontrivial scoping rules. Explain how an AG such as that in Figure 4.14
Your solution to the previous exercise probably doesn’t generalize to languages with nontrivial scoping rules. Explain how an AG such as that in Figure 4.14 might be modified to use a global symbol table similar to the one described in Section C 3.4.1. Among other things, you should consider nested scopes, the hiding of names in outer scopes, and the requirement (not enforced by the table of Section C 3.4.1) that variables be declared before they are used.
Figure 4.14:
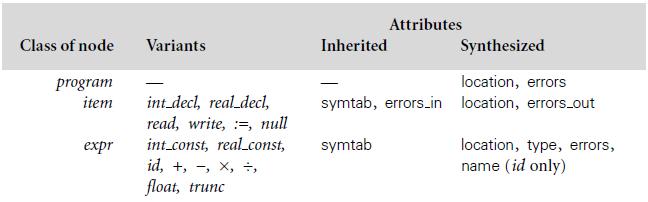
Attributes Class of node Variants Inherited Synthesized location, errors program item int decl, real_decl, read, write, :=, null int.const, real_const, id, +, -, x, , symtab, errors.in location, errors_out xpr symtab location, type, errors, name (id only) float, trunc
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The key idea is to include an indication of scope referencing environment in each node of the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


