Living cells convert energy derived from sunlight or combustion of food into energy-rich ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecules.
Question:
Living cells convert energy derived from sunlight or combustion of food into energy-rich ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecules. For ATP synthesis, ΔG = +34.5 kJ/mol. This energy is then made available to the cell when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP (adenosine diphosphate). In animals, ATP is synthesized when protons pass through a complex enzyme in the mitochondrial membrane.17 Two factors account for the movement of protons through this enzyme into the mitochondrion (see the figure): (1) [H+] is higher outside the mitochondrion than inside because protons are pumped out of the mitochondrion by enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of food. (2) The inside of the mitochondrion is negatively charged with respect to the outside.
(a) The synthesis of one ATP molecule requires 2H+ to pass through the phosphorylation enzyme. The difference in free energy when a molecule travels from a region of high activity to a region of low activity is
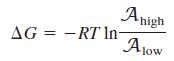
How big must the pH difference be (at 298 K) if the passage of two protons is to provide enough energy to synthesize one ATP molecule?
(b) pH differences this large have not been observed in mitochondria. How great an electric potential difference between inside and outside is necessary for the movement of two protons to provide energy to synthesize ATP? In answering this question, neglect any contribution from the pH difference.
Step by Step Answer:






