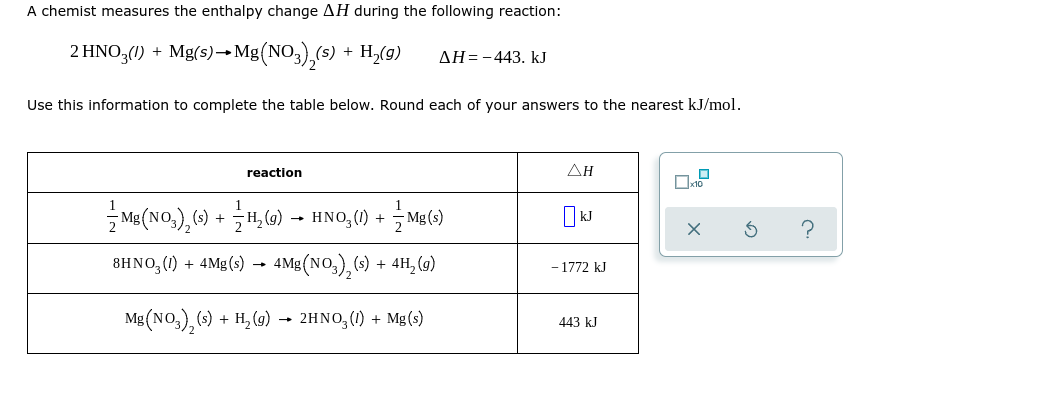
Question: #1 #2 #2 Option choice: Positive, Negative, or unknown A chemist measures the enthalpy change AH during the following reaction: 2 HNO3(1) + Mg(s) +
#1
#2 #2 Option choice: Positive, Negative, or unknown
#2 Option choice: Positive, Negative, or unknown
A chemist measures the enthalpy change AH during the following reaction: 2 HNO3(1) + Mg(s) + Mg(NO3),(s) + H (9) AH=-443. kJ Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ/mol. reaction AH x ? Mg(N0,),(s) + 3 H, (g) HN0,() + Mg(s) 8HNO, (1) + 4Mg(s) 4Mg(NO3), (s) + 4H, (9) - 1772 kJ Mg(NO3),(s) + H2(g) 2HNO3(1) + Mg(s) 443 kJ Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions AH is [pick one y A This reaction is endothermic and proceeds slower at temperatures below 62. C. AS is (pick one) AH is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below -40. C. AS is (pick one) AH is (pick one) The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below - 26. C. AS is (pick one) $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


