Question: 1 / 2 - 91% + H ROCEDURE To calculate the kinetic energy, the velocity of the ball needs to be known. From the given
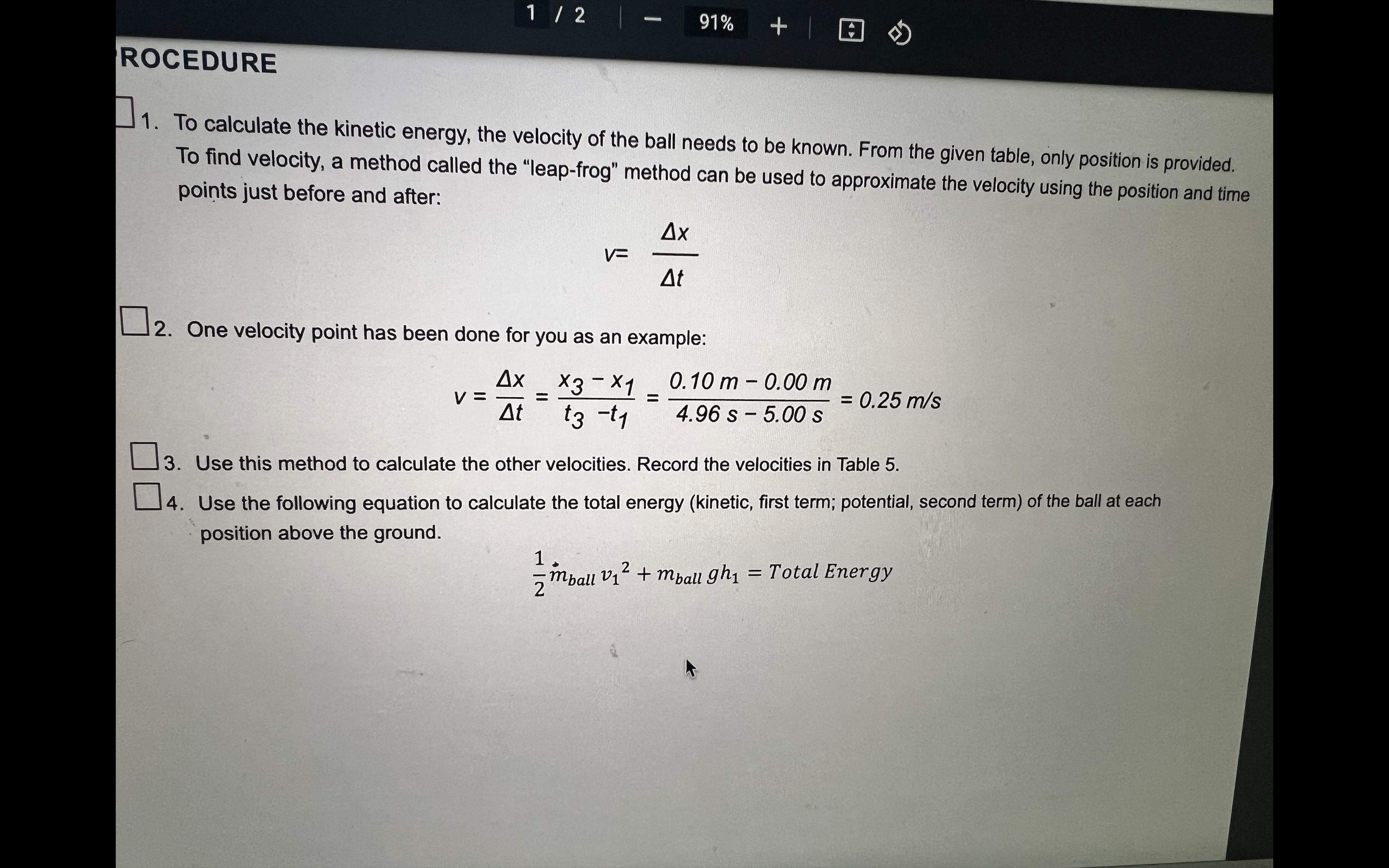
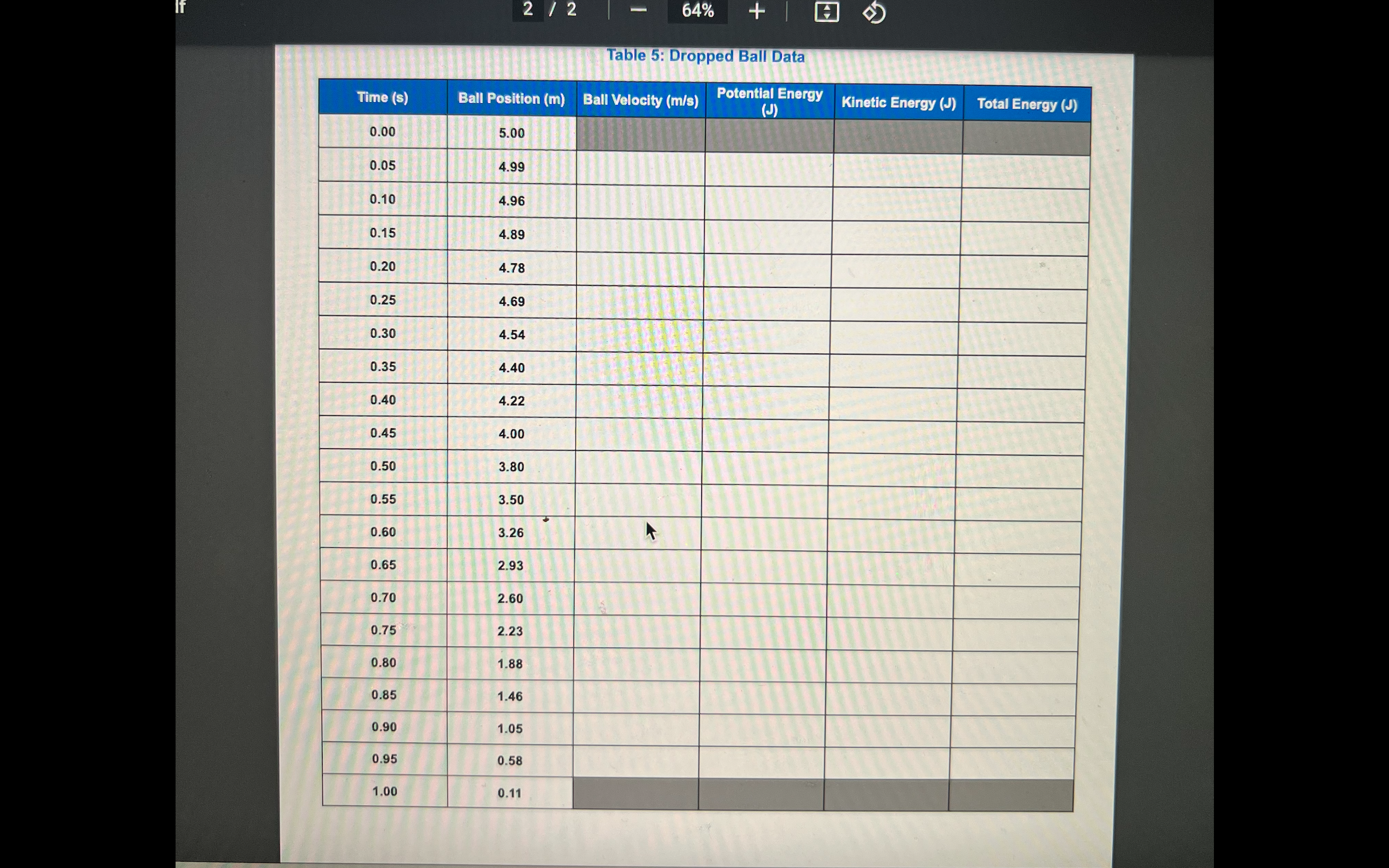
1 / 2 - 91% + H ROCEDURE To calculate the kinetic energy, the velocity of the ball needs to be known. From the given table, only position is provided. To find velocity, a method called the "leap-frog" method can be used to approximate the velocity using the position and time points just before and after: Ax V= At 2. One velocity point has been done for you as an example: Ax _X3 - X1 _ 0.10 m - 0.00 m V = = 0.25 m/s At 13 -ty 4.96 s - 5.00 s 3. Use this method to calculate the other velocities. Record the velocities in Table 5. 4. Use the following equation to calculate the total energy (kinetic, first term; potential, second term) of the ball at each position above the ground. mball v12 + mbaugh] = Total Energy2/2 - 64% + Table 5: Dropped Ball Data Time (s) Ball Position (m) Ball Velocity (m/s) Potential Energy (J) Kinetic Energy (J) Total Energy (J) 0.00 5.00 0.05 4.99 0.10 4.96 0.15 4.89 0.20 4.78 0.25 4.69 0.30 4.54 0.35 4.40 0.40 4.22 0.45 4.00 0.50 3.80 0.55 3.50 0.60 3.26 0.65 2.93 0.70 2.60 0.75 2.23 0.80 1.88 0.85 1.46 0.90 1.05 0.95 0.58 1.00 0.11Post-Lab Questions 1. Graph the potential energy, kinetic energy, and total energy of the ball. Handwrite your name next to your graph. straighterline Lab 6 Work & Conservation of Energy PHY250L 2. Describe the shape of each graph. Click here to enter text
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


