Question: 1 . A cost - allocation base: a . links indirect costs to cost objects. b . traces the direct costs and pools them. c
A costallocation base:
a links indirect costs to cost objects.
b traces the direct costs and pools them.
c serves as a base for determining the period costs.
d assigns direct costs to cost objects.
Which of the following is true of a jobcosting system?
a It is mostly suitable for companies that produce identical products.
b Jobcosting systems accumulate costs separately for each product or service.
c It calculates the perunit cost as the average unit cost that applies to all units produced.
d It is not considered suitable for service organizations.
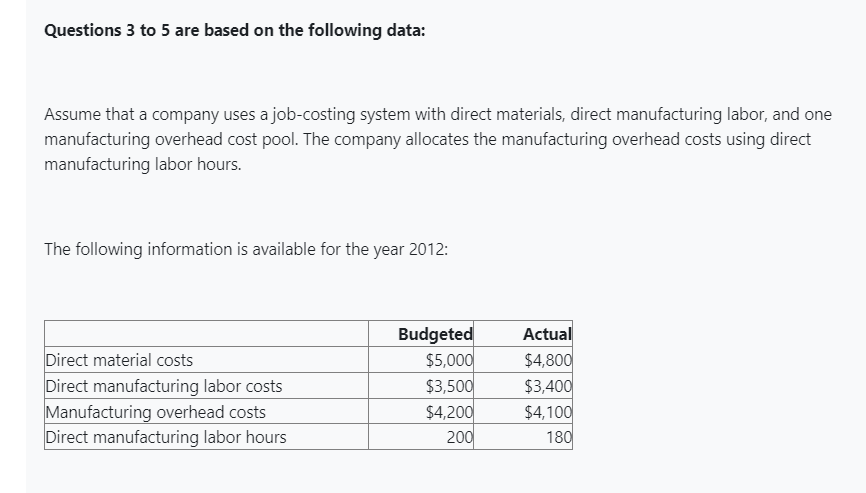
Questions to are based on the following data:
Assume that a company uses a jobcosting system with direct materials, direct manufacturing labor, and one manufacturing overhead cost pool. The company allocates the manufacturing overhead costs using direct manufacturing labor hours.
The following information is available for the year :
Budgeted
Actual
Direct material costs
$
$
Direct manufacturing labor costs
$
$
Manufacturing overhead costs
$
$
Direct manufacturing labor hours
What is the budgeted manufacturing overhead rate of the year
a $
b $
c $
d $
What is the actual manufacturing overhead rate of the year
a $
b $
c $
d $
If the actual direct manufacturing labor hours were hours, calculate the total manufacturing costs of the job as per normal costing.
a $
b $
c $
d $
Which of the following companies is most likely to require the use of job costing?
a A soda manufacturer
b An oil refinery
c A glass manufacturer
d An audit firm
Which of the following is true of under allocated indirect costs?
a They are calculated by subtracting indirect cost allocated from actual direct costs incurred.
b They occur when the allocated amount of indirect costs in an accounting period is greater than the incurred amount.
c They cannot be adjusted by using the writeoff to workinprocess approach.
d They occur when the actual manufacturing overhead costs are greater than the allocated amount.
The overallocated overhead according to the proration approach is:
a spread among ending workinprocess inventory, finished goods inventory, and cost of goods sold.
b added to the cost of goods sold of the current year.
c restated in the general ledger and jobcost records to represent actual cost rates rather than budgeted cost rates.
d included in the materials inventory as the manufacturing overhead costs include material inventory.
The manufacturing overhead allocated to job X was $ However, the actual manufacturing overhead at the end of the year was determined to be $ By how much percent is the job cost under allocated or overallocated?
a; under allocated
b; under allocated
c; overallocated
d; overallocated
Faceoff cosmetic clinic budgets total directlabor costs of $ total indirect costs of $ and total direct laborhours of Calculate the budgeted indirectcost rate for the service company if it uses direct labor costs as the allocation base.
a $
b $
c $
d $Questions to are based on the following data:
Assume that a company uses a jobcosting system with direct materials, direct manufacturing labor, and one
manufacturing overhead cost pool. The company allocates the manufacturing overhead costs using direct
manufacturing labor hours.
The following information is available for the year :
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


