Question: 1. (a) Prove or give a counter example: If A UB = AUG, then B = C. (b) Simplify AU( BU ((AU B) nC)) using

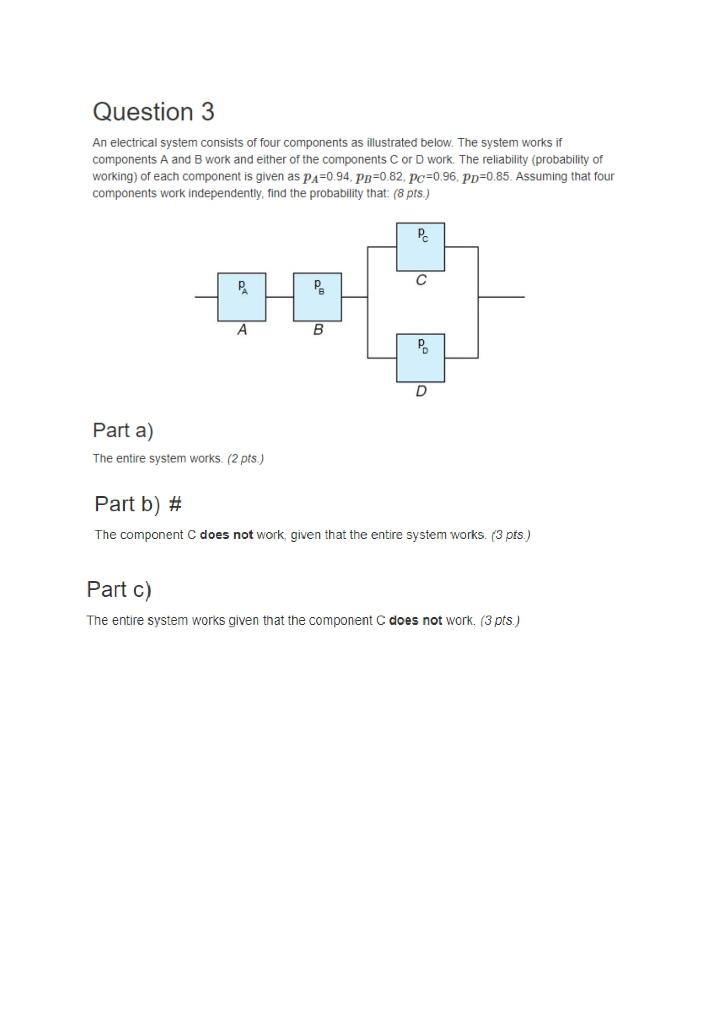

1. (a) Prove or give a counter example: If A UB = AUG, then B = C. (b) Simplify AU( BU ((AU B) nC)) using basic set operations. Do not use Venn diagrams (except, perhaps, to check your result)! (c) Let A, B, C, and D be subsets of S. Using set operations (C, 3,0, U,"), express the situation that two or fewer (e.g., exactly two, exactly one, or exactly none) of (A, B, C, D) occur. You can use Venn diagrams to help visualize the problem, but your answer must be expressed using set operations (e.g., An B).Question 3 An electrical system consists of four components as illustrated below. The system works if components A and B work and either of the components C or D work. The reliability (probability of working) of each component is given as pA=0.94. pp=0.82. pc=0.96, pp=0.85. Assuming that four components work independently, find the probability that: (8 pts.) PC A DO D Part a) The entire system works. (2 pts.) Part b) # The component C does not work, given that the entire system works. (3 pts.) Part c) The entire system works given that the component C does not work. (3 pts.)Problem 1 The symbol - is a set operation (like U and (). For any two subsets A, B of a universal set 12, the set A - B is defined as A-B := AnB = {All r ( A such that x ( B } As special cases, ? - A is the same set as A', and A - A is the same set as O. (Clicker Question 17 is about the set An B'. It may be worth reviewing that question.) (a) Draw a Venn Diagram for the sets A and B (assuming they partly overlap each other), and indicate the three regions corresponding to the three sets A-B, An B and B-A. (b) Is A - B always a subset of A? State the reason. (c) By using De Morgan's Law, what is the complement of A - B? Express the result by using A, B and the three basic set operations U, A and'. (d) If 2 is the sample space of a random experiment, and A and B are events, we would interpret An B as the event that A and B both occur. Interpret the event A - B in a similar way, and prove that P(A - B) = P(A) - P(AnB)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


