Question: 1. Complete the table below using the example shown above to prove that you really understand the algorithm. The first few rows have shown you
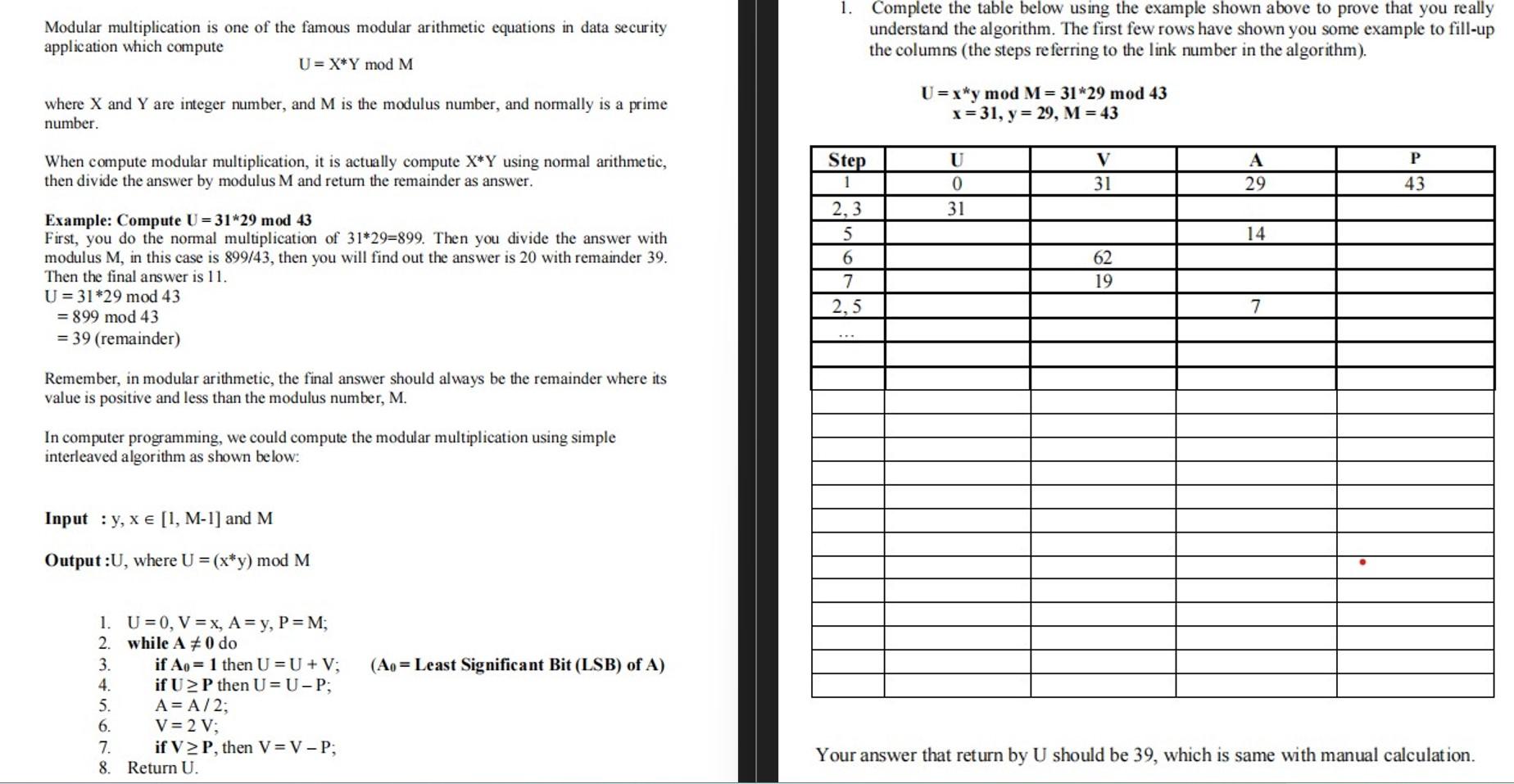
1. Complete the table below using the example shown above to prove that you really understand the algorithm. The first few rows have shown you some example to fill-up the columns (the steps referring to the link number in the algorithm). Modular multiplication is one of the famous modular arithmetic equations in data security application which compute U=XYmodM U=xymodM=3129mod43x=31,y=29,M=43 where X and Y are integer number, and M is the modulus number, and normally is a prime number. When compute modular multiplication, it is actually compute XY using normal arithmetic, then divide the answer by modulus M and retum the remainder as answer. Example: Compute U=3129mod43 First, you do the normal multiplication of 3129=899. Then you divide the answer with modulus M, in this case is 899/43, then you will find out the answer is 20 with remainder 39 . Then the final answer is 11. U=3129mod43=899mod43=39(remainder) Remember, in modular arithmetic, the final answer should always be the remainder where its value is positive and less than the modulus number, M. In computer programming, we could compute the modular multiplication using simple interleaved algorithm as shown below: Input :y,x[1,M1] and M Output :U, where U=(xy)modM 1. U=0,V=x,A=y,P=M; 2. while A=0 do 3. if A0=1 then U=U+V;(A0= Least Significant Bit (LSB) of A) 4. if UP then U=UP; 5. A=A/2; 6. V=2V; 7. if VP, then V=VP; 8. Return U. 1. Complete the table below using the example shown above to prove that you really understand the algorithm. The first few rows have shown you some example to fill-up the columns (the steps referring to the link number in the algorithm). Modular multiplication is one of the famous modular arithmetic equations in data security application which compute U=XYmodM U=xymodM=3129mod43x=31,y=29,M=43 where X and Y are integer number, and M is the modulus number, and normally is a prime number. When compute modular multiplication, it is actually compute XY using normal arithmetic, then divide the answer by modulus M and retum the remainder as answer. Example: Compute U=3129mod43 First, you do the normal multiplication of 3129=899. Then you divide the answer with modulus M, in this case is 899/43, then you will find out the answer is 20 with remainder 39 . Then the final answer is 11. U=3129mod43=899mod43=39(remainder) Remember, in modular arithmetic, the final answer should always be the remainder where its value is positive and less than the modulus number, M. In computer programming, we could compute the modular multiplication using simple interleaved algorithm as shown below: Input :y,x[1,M1] and M Output :U, where U=(xy)modM 1. U=0,V=x,A=y,P=M; 2. while A=0 do 3. if A0=1 then U=U+V;(A0= Least Significant Bit (LSB) of A) 4. if UP then U=UP; 5. A=A/2; 6. V=2V; 7. if VP, then V=VP; 8. Return U
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


