Question: 1. * Consider a cipher system (Gen, Enc, Dec). Let the message space, key space and cipher space be the set consisting of 3-bit vectors.
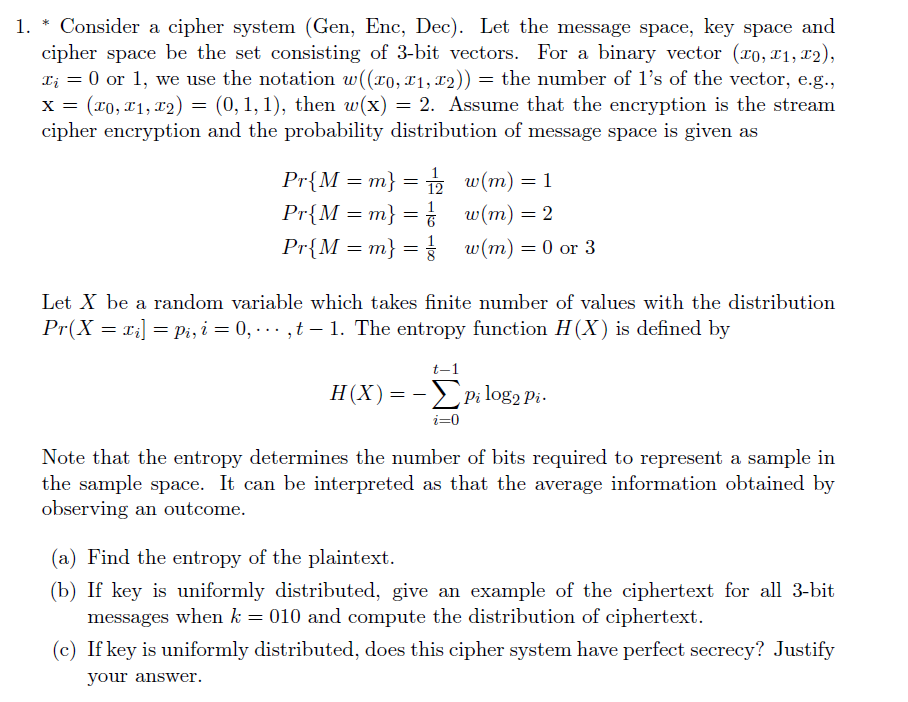
1. * Consider a cipher system (Gen, Enc, Dec). Let the message space, key space and cipher space be the set consisting of 3-bit vectors. For a binary vector (ro, r1, 12), = 0 or 1, we use the notation w((10,11,12)) = the number of l's of the vector. e.g x (10,11,12) = (0,1,1), then w(x) = 2. Assume that the encryption is the stream cipher encryption and the probability distribution of message space is given as Pr(M = m} = w(m) = 0 or 3 Let X be a random variable which takes finite number of values with the distribution Pr(X 1i] = Pi, 2 0, . . . ,t-1. The entropy function H (X) is defined by i-0 Note that the entropy determines the number of bits required to represent a sample in the sample space. It can be interpreted as that the average information obtained by observing an outcome. (a) Find the entropy of the plaintext (b) If key is uniformly distributed, give an example of the ciphertext for all 3-bit messages when k 010 and compute the distribution of ciphertext. (c) If key is uniformly distributed, does this cipher system have perfect secrecy? Justify your answer. 1. * Consider a cipher system (Gen, Enc, Dec). Let the message space, key space and cipher space be the set consisting of 3-bit vectors. For a binary vector (ro, r1, 12), = 0 or 1, we use the notation w((10,11,12)) = the number of l's of the vector. e.g x (10,11,12) = (0,1,1), then w(x) = 2. Assume that the encryption is the stream cipher encryption and the probability distribution of message space is given as Pr(M = m} = w(m) = 0 or 3 Let X be a random variable which takes finite number of values with the distribution Pr(X 1i] = Pi, 2 0, . . . ,t-1. The entropy function H (X) is defined by i-0 Note that the entropy determines the number of bits required to represent a sample in the sample space. It can be interpreted as that the average information obtained by observing an outcome. (a) Find the entropy of the plaintext (b) If key is uniformly distributed, give an example of the ciphertext for all 3-bit messages when k 010 and compute the distribution of ciphertext. (c) If key is uniformly distributed, does this cipher system have perfect secrecy? Justify your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


