Question: 1. Consider lD. steady-state conduction in a composite wall. The wall consists of two layers, A and B. with thickness ofLA = 0.1 m and
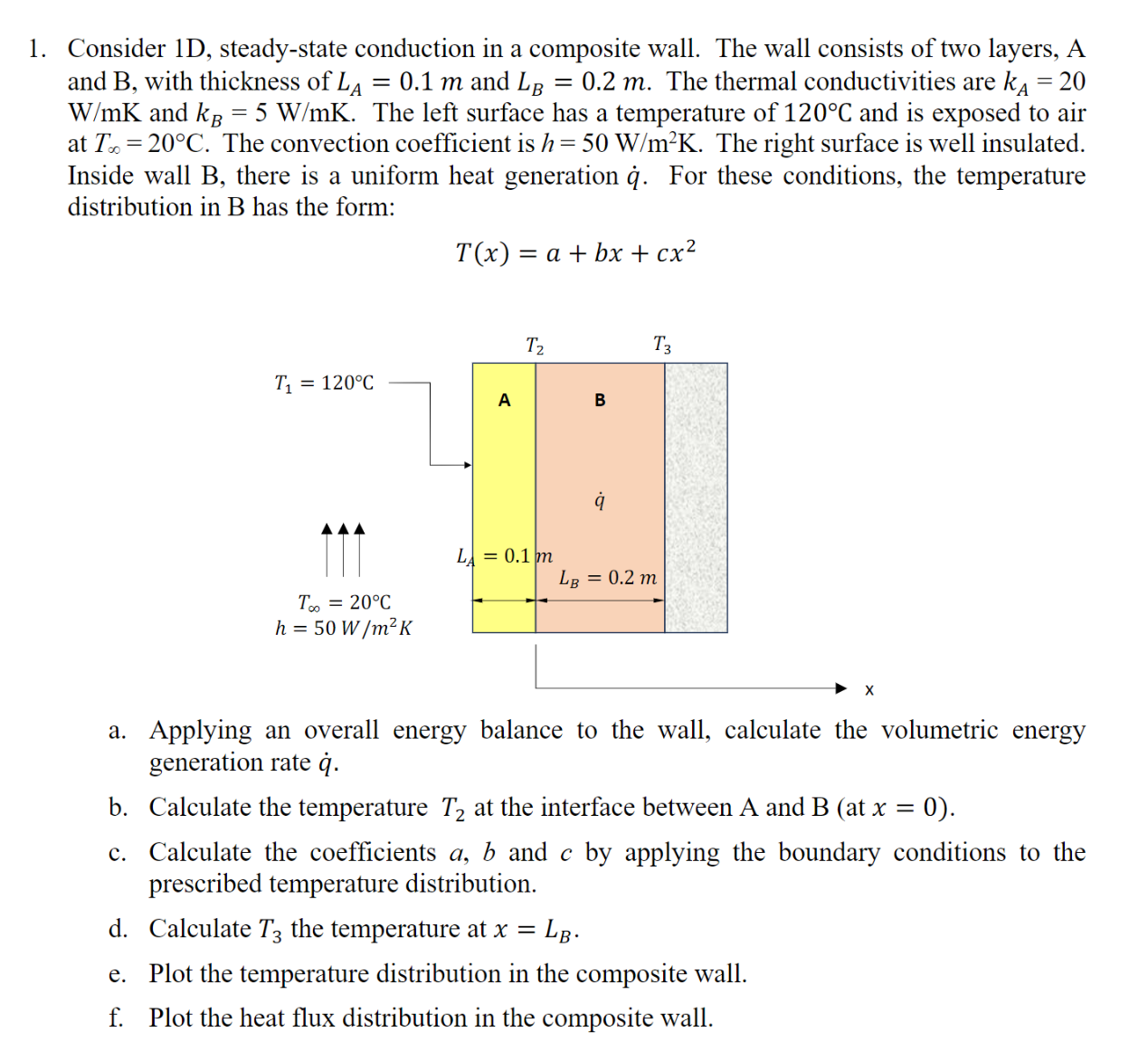
1. Consider lD. steady-state conduction in a composite wall. The wall consists of two layers, A and B. with thickness ofLA = 0.1 m and LB = 0.2 m. The thermal conductivities are kA : 20 W/mK and k3 : 5 W/mK. The left surface has a temperature of 120C and is exposed to air at T3 = 20C, The convection coefficient is h 2 50 W/mgK. The right surface is well insulated Inside wall B. there is a uniform heat generation 5;. For these conditions, the temperature distribution in B has the form: T(x) = a +bx+cx2 T1 : 120C 7 iii To. = 20C h = 50 W/mZK l . . :1. Applying an overall energy balance to the wall. calculate the volumetric energy generation rate 6]. b. Calculate the temperature T2 at the interface between A and B (at x = 0). c. Calculate the coefficients a, b and c by applying the boundary conditions to the prescribed temperature distribution. d. Calculate T3 the temperature at x = 1.3. e. Plot the temperature distribution in the composite wall. f. Plot the heat ux distribution in the composite wall
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


