Question: 1. Consider the following circular city model with an externality. Consumers (normalized to one) are distributed uniformly around a circle with perimeter length of one.
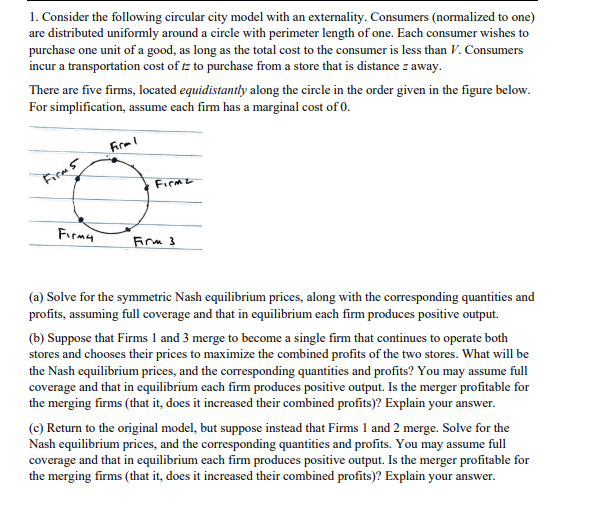
1. Consider the following circular city model with an externality. Consumers (normalized to one) are distributed uniformly around a circle with perimeter length of one. Each consumer wishes to purchase one unit of a good, as long as the total cost to the consumer is less than V. Consumers incur a transportation cost of tz to purchase from a store that is distance z away. There are five firms, located equidistantly along the circle in the order given in the figure below. For simplification, assume each firm has a marginal cost of 0 . (a) Solve for the symmetric Nash equilibrium prices, along with the corresponding quantities and profits, assuming full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. (b) Suppose that Firms 1 and 3 merge to become a single firm that continues to operate both stores and chooses their prices to maximize the combined profits of the two stores. What will be the Nash equilibrium prices, and the corresponding quantities and profits? You may assume full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. Is the merger profitable for the merging firms (that it, does it increased their combined profits)? Explain your answer. (c) Return to the original model, but suppose instead that Firms 1 and 2 merge. Solve for the Nash equilibrium prices, and the corresponding quantities and profits. You may assume full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. Is the merger profitable for the merging firms (that it, does it increased their combined profits)? Explain your answer. 1. Consider the following circular city model with an externality. Consumers (normalized to one) are distributed uniformly around a circle with perimeter length of one. Each consumer wishes to purchase one unit of a good, as long as the total cost to the consumer is less than V. Consumers incur a transportation cost of tz to purchase from a store that is distance z away. There are five firms, located equidistantly along the circle in the order given in the figure below. For simplification, assume each firm has a marginal cost of 0 . (a) Solve for the symmetric Nash equilibrium prices, along with the corresponding quantities and profits, assuming full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. (b) Suppose that Firms 1 and 3 merge to become a single firm that continues to operate both stores and chooses their prices to maximize the combined profits of the two stores. What will be the Nash equilibrium prices, and the corresponding quantities and profits? You may assume full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. Is the merger profitable for the merging firms (that it, does it increased their combined profits)? Explain your answer. (c) Return to the original model, but suppose instead that Firms 1 and 2 merge. Solve for the Nash equilibrium prices, and the corresponding quantities and profits. You may assume full coverage and that in equilibrium each firm produces positive output. Is the merger profitable for the merging firms (that it, does it increased their combined profits)? Explain your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


