Question: 1. Digital Systems generally represent 'human' information via some sort of code. For example, BCD is a binary coded representation of the decimal values 0
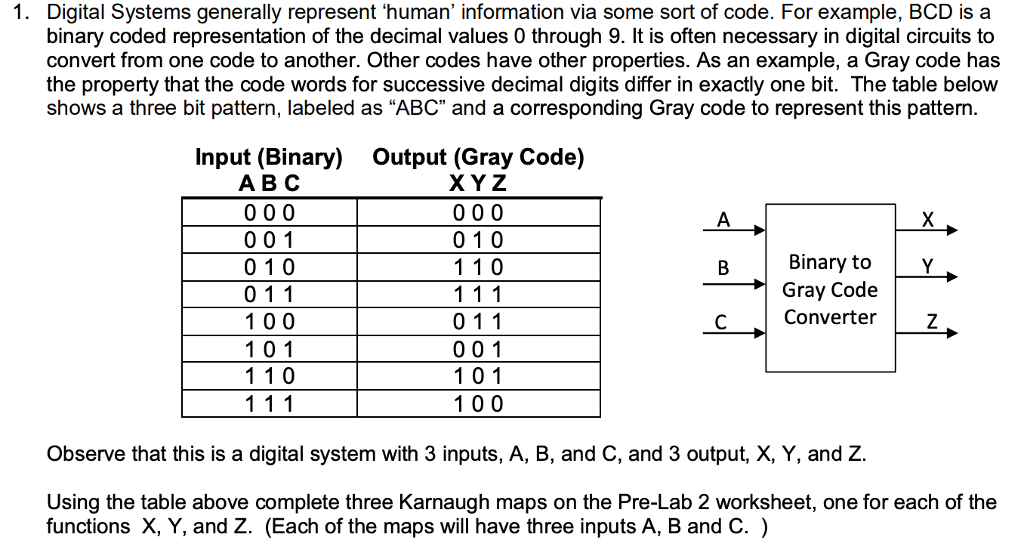

1. Digital Systems generally represent 'human' information via some sort of code. For example, BCD is a binary coded representation of the decimal values 0 through 9. It is often necessary in digital circuits to convert from one code to another. Other codes have other properties. As an example, a Gray code has the property that the code words for successive decimal digits differ in exactly one bit. The table below shows a three bit pattern, labeled as "ABC" and a corresponding Gray code to represent this pattern Input (Binary) ABC Output (Gray Code) X Y Z 001 01 0 0 11 100 1 01 1 10 010 1 10 Binary to Y Gray Codee Converter 0 11 001 1 01 1 00 Observe that this is a digital system with 3 inputs, A, B, and C, and 3 output, X, Y, and Z. Using the table above complete three Karnaugh maps on the Pre-Lab 2 worksheet, one for each of the functions X, Y, and Z. (Each of the maps will have three inputs A, B and C.) 2. Write the simplified equations for X, Y, and Z on the Pre-Lab 2 worksheet. 3. Draw a circuit that realizes X, Y, and Z using only 2-input NAND gates and Inverters. Recall that this should be done by: Using Boolean Algebra, likely the distributive law, to ensure that all operations can be done using two-input gates only, then Drawing the circuit using 2-input AND and OR gates and inverters, then Converting AND gates and OR gates to NAND gates. You can use at most 8 NAND gates and 6 inverters. Using the Data Sheets for the 7432 and 7400 chips, label each gate input and output with the pin of the chip that will be used in your lab construction. 1. Digital Systems generally represent 'human' information via some sort of code. For example, BCD is a binary coded representation of the decimal values 0 through 9. It is often necessary in digital circuits to convert from one code to another. Other codes have other properties. As an example, a Gray code has the property that the code words for successive decimal digits differ in exactly one bit. The table below shows a three bit pattern, labeled as "ABC" and a corresponding Gray code to represent this pattern Input (Binary) ABC Output (Gray Code) X Y Z 001 01 0 0 11 100 1 01 1 10 010 1 10 Binary to Y Gray Codee Converter 0 11 001 1 01 1 00 Observe that this is a digital system with 3 inputs, A, B, and C, and 3 output, X, Y, and Z. Using the table above complete three Karnaugh maps on the Pre-Lab 2 worksheet, one for each of the functions X, Y, and Z. (Each of the maps will have three inputs A, B and C.) 2. Write the simplified equations for X, Y, and Z on the Pre-Lab 2 worksheet. 3. Draw a circuit that realizes X, Y, and Z using only 2-input NAND gates and Inverters. Recall that this should be done by: Using Boolean Algebra, likely the distributive law, to ensure that all operations can be done using two-input gates only, then Drawing the circuit using 2-input AND and OR gates and inverters, then Converting AND gates and OR gates to NAND gates. You can use at most 8 NAND gates and 6 inverters. Using the Data Sheets for the 7432 and 7400 chips, label each gate input and output with the pin of the chip that will be used in your lab construction
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


