Question: 1 Gaussian Class-Conditional distribution (a) Consider a binary classifier (i.e. y E [0,1). Suppose the class conditional distribution, p(r()y(m)j is a Gaussian with mean ?
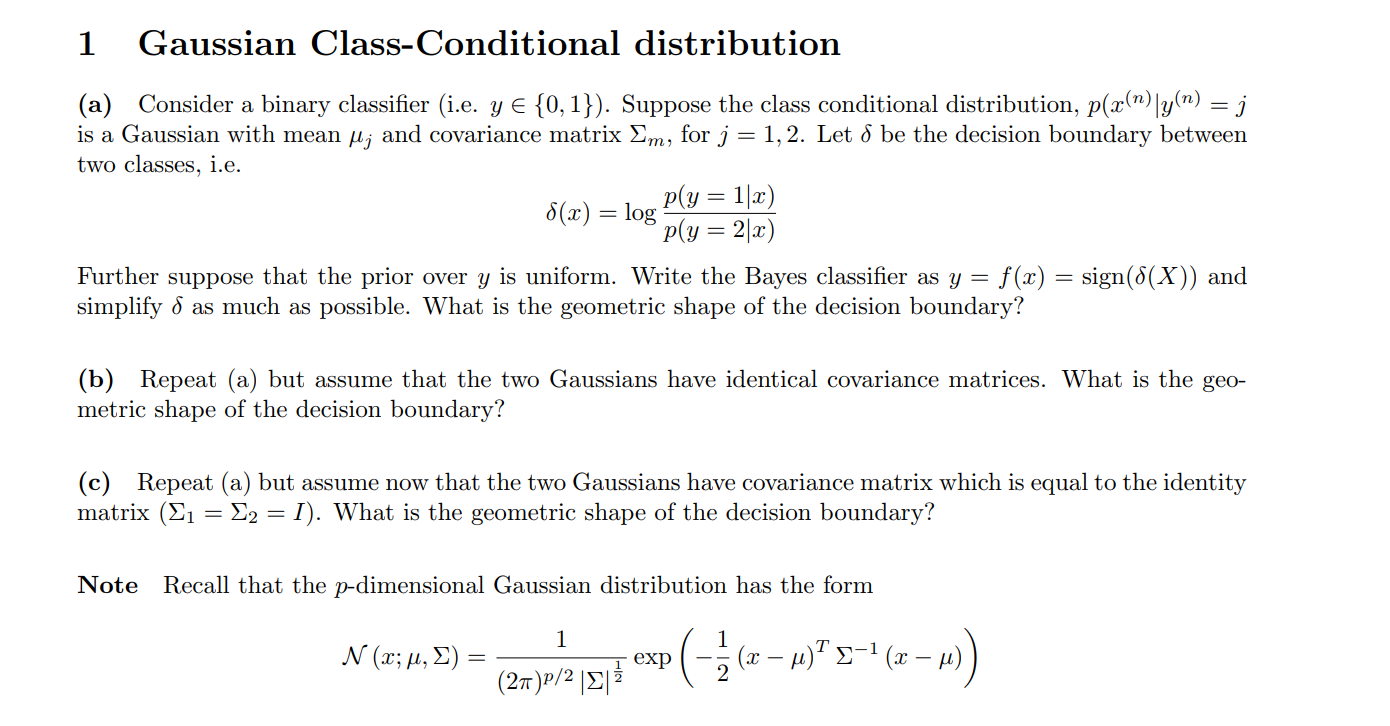
1 Gaussian Class-Conditional distribution (a) Consider a binary classifier (i.e. y E [0,1). Suppose the class conditional distribution, p(r(")y(m)j is a Gaussian with mean ? j and covariance matrix ???, for j-1.2 Let be the decision boundary between two classes, i.e. Further suppose that the prior over y is uniform. Write the Bayes classifier as y- f(x) -sign(5(X)) and simplify 6 as much as possible. What is the geometric shape of the decision boundary? (b) Repeat (a) but assume that the two Gaussians have identical covariance matrices. What is the geo- metric shape of the decision boundary? (c) Repeat (a) but assume now that the two Gaussians have covariance matrix which is equal to the identity matrix (21 -22- I). What is the geometric shape of the decision boundary? Note Recall that the p-dimensional Gaussian distribution has the form (27)p/2 ???? 1 Gaussian Class-Conditional distribution (a) Consider a binary classifier (i.e. y E [0,1). Suppose the class conditional distribution, p(r(")y(m)j is a Gaussian with mean ? j and covariance matrix ???, for j-1.2 Let be the decision boundary between two classes, i.e. Further suppose that the prior over y is uniform. Write the Bayes classifier as y- f(x) -sign(5(X)) and simplify 6 as much as possible. What is the geometric shape of the decision boundary? (b) Repeat (a) but assume that the two Gaussians have identical covariance matrices. What is the geo- metric shape of the decision boundary? (c) Repeat (a) but assume now that the two Gaussians have covariance matrix which is equal to the identity matrix (21 -22- I). What is the geometric shape of the decision boundary? Note Recall that the p-dimensional Gaussian distribution has the form (27)p/2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


