Question: 1. In Week 2's notes, a way is shown in which the integers 0 through 255 can be represented in an 8-bit storage device (a
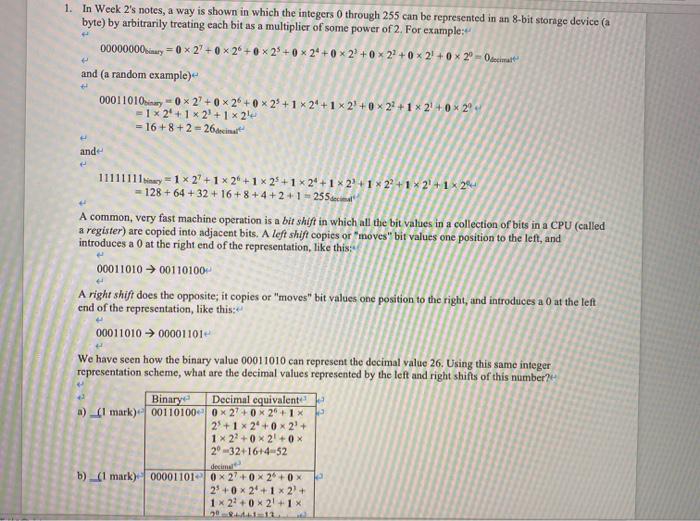

1. In Week 2's notes, a way is shown in which the integers 0 through 255 can be represented in an 8-bit storage device (a byte) by arbitrarily treating each bit as a multiplier of some power of 2. For example: 00000000nry = 0 x 2 + 0 2 + 25 +0 * 24+0 * 2+0 22+0 * 2! +0 20 -Odeiner and (a random example) 00011010binary 029+0 26 + 0* 25 + 1 24 + 1 X 2+23 +1 * 21 + 0 x 24 - 1 * 2 + 1 x 2 + 1 x 20 = 16+8+2 = 26decimale ande 11111111y = 1 * 2? + 1 2 + 1 x 23 +1 * 24+ 1 * 2 + 1 * 22+1 * 21 + 1*24 128 +64 + 32 + 16 +8+4 +2+1 255cm A common, very fast machine operation is a bit shift in which all the bit values in a collection of bits in a CPU (called a register) are copied into adjacent bits. A left shift copies or "moves" bit values one position to the left, and introduces a 0 at the right end of the representation, like this: 00011010 00110100 A right shift does the opposite; it copies or "moves" bit values one position to the right, and introduces a 0 at the left end of the representation, like this: 00011010 00001101 We have seen how the binary value 00011010 can represent the decimal value 26. Using this same integer representation scheme, what are the decimal values represented by the left and right shifts of this number? Binary Decimal equivalente a) (1 mark) 001101000 x 270 x 25+1 2 + 1 x 24 +0* 2+ 1x2 + 0x2 + 0x 29.32+16+4-52 b) _(1 mark) 000011010 0% 27+0 2*+ 0x 2 + 0 x 2 + 1x2 + 1x 2 + 0x2 + 1 c) (2 marks) in the box below, tell me how these two shifted values relate to the original value of 26decimal: +
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


