Question: 1. Install Django on your machine. If you don't have it already, you will need to install Python and pip (the Python package manager) first.

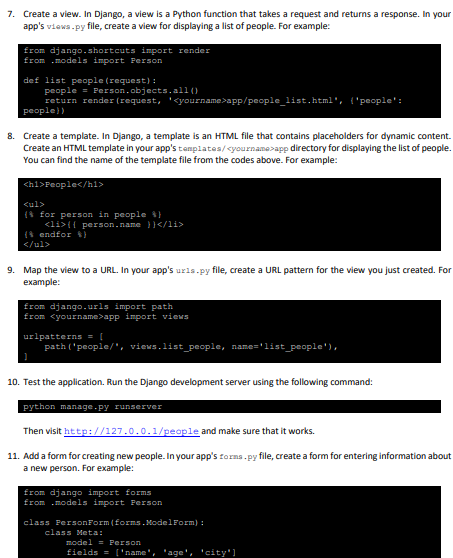
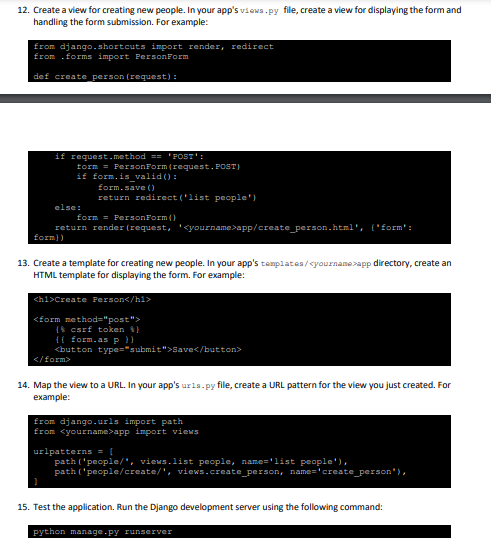
1. Install Django on your machine. If you don't have it already, you will need to install Python and pip (the Python package manager) first. You can then install Django using pip: pip install django 2. Create a new Django project. Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where you want to create the project. Then run the following command: django-admin startproject project This will create a new Django project with your name, for example "johnproject". 3. Create a new Django app. Within your project, you will need to create a new app to hold your code. Run the following command: python manage.py startapp app This will create a new app with your name, for example "johnapp" within your project. 4. Define a model. In Django, a model is a class that represents a table in the database. In your app's node1 . py file, define a model for storing information about a person. For example: fron django . dh import models class Ferson (models. Wodel) : name = models. Chargield(max length=100) age = models. IntegerField() city = models. CharEield(max_length=100) 5. Add your app to the INSTALLED_APPS in the settings.py file using this code: 'app - apps. appConfig' 6. Create a database migration. After defining your model, you will need to create a database migration to create the corresponding table in the database. Run the following command: python manage.py makemigrations 6. Run the migration. Once you have created the migration, you will need to apply it to the database. Run the following command: 7. Create a view. In Django, a view is a Python function that takes a request and returns a response. In your app's viows -py file, create a view for displaying a list of people. For example: 8. Create a template. In Django, a template is an HTML file that contains placeholders for dynamic content. Create an HTML template in your app's templates/ app directory for displaying the list of people; You can find the name of the template file from the codes above. For example: 9. Map the view to a URL. In your app's ur1s.py file, create a URL pattern for the view you just created. For example: from django.urls import path from app inport views urlpatterns = [ path ('people/', views.1ist_people, name='list_people'), 10. Test the application. Run the Django development server using the following command: python manage.py runserver Then visit http://127.0.0.1/people and make sure that it works. 11. Add a form for creating new people. In your app's torns . py file, create a form for entering information about a new person. For example: from django import forms from . models import Ferson class FersonForm (forms.ModelForm) : class Meta: model = Person fields = ['name" "age', 'city"] 12. Create a view for creating new people. In your app's views. py file, create a view for displaying the form and handling the form submission. For example: from django - shortcuts import render, redirect from - forms import Personform def create person (request) : 13. Create a template for creating new people. In your app's templates/ yournamerapp directory, create an HTML template for displaying the form. For example: 14. Map the view to a URL. In your app's ur1s . py file, create a URL pattern for the view you just created. For example: from django.urls import path from app import views urlpatterns = 1 path ('people/", views.1ist people, name='list people'), path ('people/create/', views.create_person, name='create_person"), 1) 15. Test the application. Run the Django development server using the following command






