Question: 1) Modify the One-dimensional Arrays Example a. The Java code can be found on Blackboard in our Sample Program - Code section b. I showed


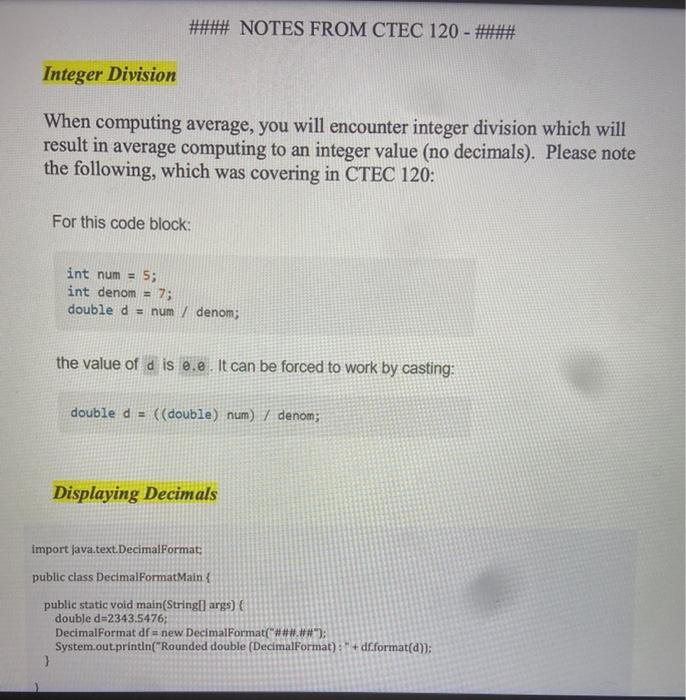
1) Modify the "One-dimensional Arrays Example" a. The Java code can be found on Blackboard in our Sample Program - Code section b. I showed the code at the end of Monday's class, using Netbeans 2) Add the following functionally (methods NOT needed) a. MUST use for loop(s) and arrays for the next 3 items (hint: our book covers the 1st two specifically): i. Compute and display the sum of all the integers in the array ii. Compute and display the average of all the integers in the array iii. Determine the # of passing grades (70 and above) and display the total # of passing grades in the array 3) Sample Output TU Please enter grade 1 of 3 0 to 100 Please enter grade 2 of 3 0 to 100 Please enter grade 3 of 3 0 to 100 92 83 5592 Sum 230 Average - 76.67 of passing grades - 2 3) Sample Output run: Please enter grade 1 of 3 0 to 100 83 Please enter grade 2 of 3.0 to 100 55 Please enter grade 3 of 3 0 to 100 92 83 55 92 Sum = 230 Average = 76.67 # of passing grades =- 2 BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 6 seconds) #### NOTES FROM CTEC 120 - #### Integer Division When computing average, you will encounter integer division which will result in average computing to an integer value (no decimals). Please note the following, which was covering in CTEC 120: #### NOTES FROM CTEC 120 - ##### Integer Division When computing average, you will encounter integer division which will result in average computing to an integer value (no decimals). Please note the following, which was covering in CTEC 120: For this code block: int num = 5; int denom = 7; double d = num / denom; the value of d is e.e. It can be forced to work by casting: double d = ((double) num) / denom; Displaying Decimals import java.text.DecimalFormat: public class DecimalformatMain public static void main(String[] args) double d=2343.5476; DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#*#.##"); System.out.println("Rounded double (DecimalFormat) : " + df.format(a)); }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


