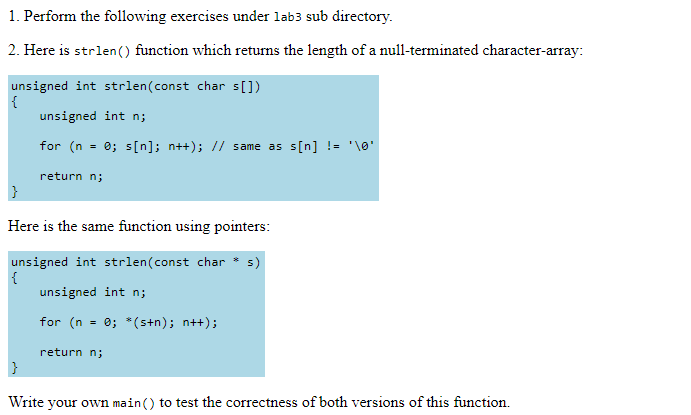
Question: 1. Perform the following exercises under lab3 sub directory. 2. Here is strlen() function which returns the length of a null-terminated character-array unsigned int strlen

![int strlen (const char s[]) unsigned int n; for (n = 0;](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f01786e725b_69466f0178676560.jpg)
![s[n]; return n; n++); // same as s[n] != 'Ve. Here is](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f0178784d9a_69566f01787271a0.jpg)

1. Perform the following exercises under lab3 sub directory. 2. Here is strlen() function which returns the length of a null-terminated character-array unsigned int strlen (const char s[]) unsigned int n; for (n = 0; s[n]; return n; n++); // same as s[n] != 'Ve. Here is the same function using pointers: unsigned int strlen(const char* s) unsigned int n; for (n = 0; .(s+n); return n; n++); Write your own main() to test the correctness of both versions of this function
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


