Question: 1 . PHYSICAL MODELING: DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS and SIMILITUDE In the laminar flow of a viscous fluid through a horizontal pipe, the pressure drop (
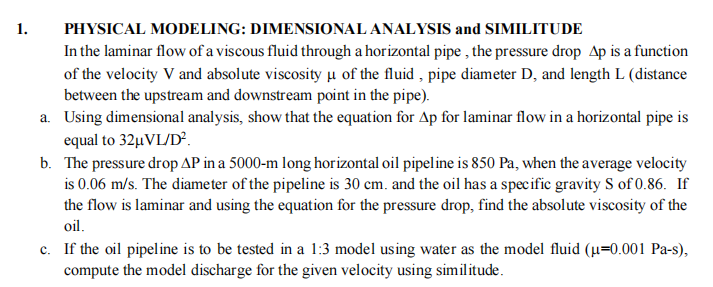
PHYSICAL MODELING: DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS and SIMILITUDE
In the laminar flow of a viscous fluid through a horizontal pipe, the pressure drop Delta mathrmp is a function of the velocity V and absolute viscosity mu of the fluid, pipe diameter D and length L distance between the upstream and downstream point in the pipe
a Using dimensional analysis, show that the equation for Delta mathrmp for laminar flow in a horizontal pipe is equal to mu mathrmVLmathrmD
b The pressure drop Delta mathrmP in a mathrmm long horizontal oil pipel ine is Pa when the average velocity is mathrm~mmathrms The diameter of the pipeline is cm and the oil has a specific gravity S of If the flow is laminar and using the equation for the pressure drop, find the absolute viscosity of the oil.
c If the oil pipeline is to be tested in a : model using water as the model fluid mumathrm~Pas compute the model discharge for the given velocity using similitude.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


