Question: 1 point 1. Which access specifier makes instance variables accessible to everybody? protected public override private 1 point 2. Which does an inspector function do?*
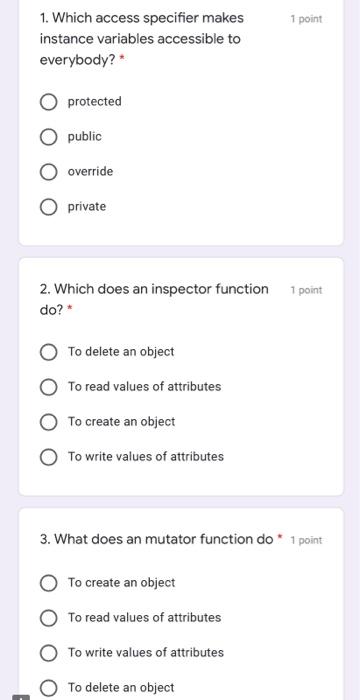
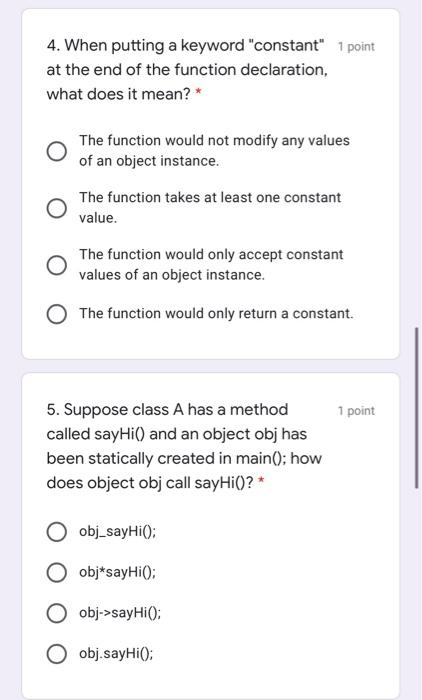
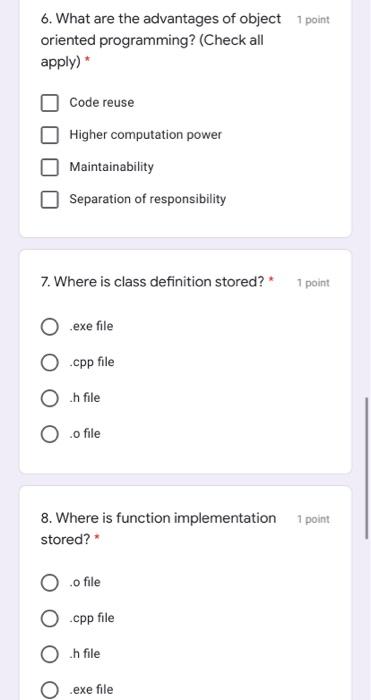
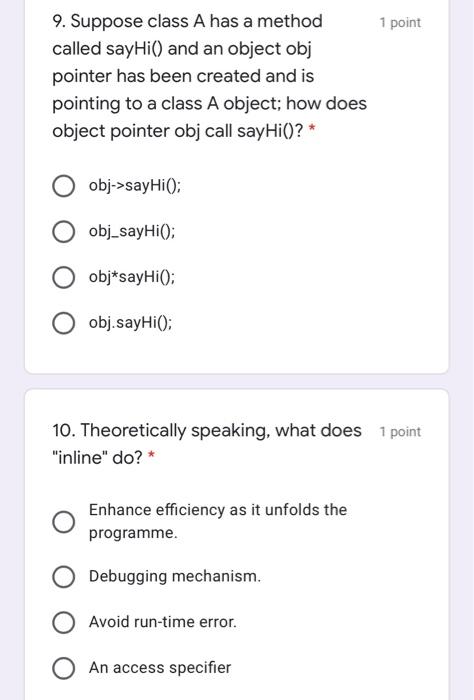
1 point 1. Which access specifier makes instance variables accessible to everybody? protected public override private 1 point 2. Which does an inspector function do?* To delete an object To read values of attributes To create an object To write values of attributes 3. What does an mutator function do * 1 point To create an object To read values of attributes To write values of attributes To delete an object 4. When putting a keyword "constant" 1 point at the end of the function declaration, what does it mean? The function would not modify any values of an object instance. The function takes at least one constant value. The function would only accept constant values of an object instance. The function would only return a constant. 1 point 5. Suppose class A has a method called sayHi() and an object obj has been statically created in main(); how does object obj call sayHi(?* obj_sayHiO); obj*sayHiO; obj->sayHio: O obj.sayHiO; 6. What are the advantages of object 1 point oriented programming? (Check all apply) * Code reuse Higher computation power Maintainability Separation of responsibility 7. Where is class definition stored? 1 point .exe file .cpp file .h file o file 8. Where is function implementation 1 point stored? o file .cpp file .h file .exe file 1 point 9. Suppose class A has a method called sayHi() and an object obj pointer has been created and is pointing to a class A object; how does object pointer obj call say Hi()? obj->sayHiO; obj_sayHiO; obj*sayHi(); obj.sayHiO; 10. Theoretically speaking, what does 1 point "inline" do? * Enhance efficiency as it unfolds the programme. Debugging mechanism. Avoid run-time error. O An access specifier
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


