Question: 1. Provided the network schematics as shown below. A special scenario where two hosts H1, H2 send TCP and UDP traffic to the same host
1. Provided the network schematics as shown below. A special scenario where two hosts H1, H2 send TCP and UDP traffic to the same host H3 respectively both at 100MBits/s. All of the links are 100MBits/s FULL DUPLEX .
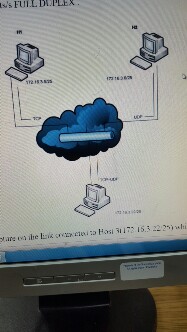
The Wireshark Capture on the link connected to Host 3(172.16.3.22/25) which is shared by both the TCP and UDP traffic is as shown below.
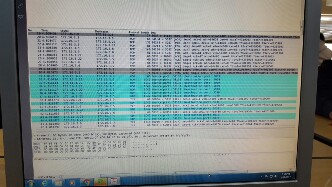
From the IO plot of both UDP and TCP, RED represents UDP whereas BLACK corresponds to TCP
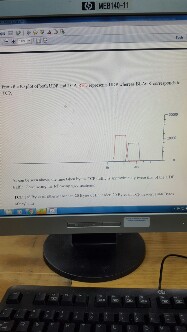
As can be seen above, the time taken by the TCP traffic is approximately twice that of the UDP traffic. Considering the following specifications:
TCP: (38 Bytes of Ethernet header, 20 Bytes of IP header, 20 Bytes of TCP header, 1460 Bytes of payload)
UDP: (38 Bytes of Ethernet header, 20 Bytes of IP header, 8 Bytes of UDP header, 1472 Bytes of payload)
Questions:
a) Calculate the theoretical Goodput of the TCP and UDP in the case of shared link?
b) What is the theoretical Goodput of the TCP traffic if only host H1 sends traffic to H3? Compare the value with the TCP good put in part a?
c) Explain the fairness situation between the TCP and UDP traffics on the shared link? Why the TCP traffic took longer for the same amount of data while both H1 and H2 started sending traffic to H3 at the same time?
2. Consider a simple AWGN (Additive white Gaussian noise) Wireless Channel. The carrier frequency is fc = 2115MHz and the channel bandwidth is f = B = 1MHz. The RX antenna
temperature can be assumed to be Ta = 1000K due to man-made noise; the RX antenna gain is always at least 0dB (worst case), and depolarization loss not more than 3dB. We want a bit error rate (BER, error probability) Pe 104 and we use 4PSK as provided in the class textbook Figure 5.13b.
a) What SNR Eb / N0 do we need?
b) For a bit-rate Rs= 500 kb/s, what is the required carrier-to-noise ratio C/N? (in dB)
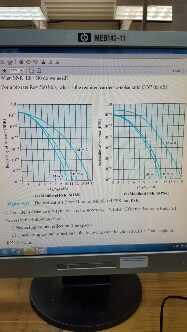
c) Consider a distance d = 1km; what is the necessary TX EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) in the following cases i) Neglecting ground reflection (free space) ii) Considering ground reflection in the following case: height of TX h1 = 30m, height of RX h2=1.5m. 3. Assume the following network scenario. Flow BA direction, all transmissions are infinitely fast, i.e. zero delay; this is often a good approximation because ACK packets are what travel in that direction and they are negligibly small. In the AB direction, we will assume that the AR1 link is infinitely fast, but the other four each have a bandwidth of 1 packet/second (and no propagation-delay component). This makes the R1R2 link thebottleneck link; any queue will now form at R1. The path bandwidth is 1 packet/second, and the RTT is 4 seconds. Questions: provided a winsize=3, complete the following table whenever there is a packet available

Note: the brief pile-up at R1 (the bottleneck link!) on startup. However, in the steady state, there is no queuing. i.e At T=3, R1 has just finished sending Data[3] as Data[4] arrives from A; R1 can begin sending packet 4 immediately. No queue will develop. Real sliding-windows protocols generally have some way of minimizing this initial pileup. 4. Find the CRC-12 code for the data sequence (message) 101010101010101010101010. Verify a zero residual with no errors on the channel. Verify failure detection when bit 3 (from the right) is in error. Show your calculations.
s's FULL DEPLEX. are ex) ibe luia av/exce: a Hosl i 170 15.3 2225) ali
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


