Question: (1) Question 1. (10 marks) Consider the risk-neutral dynamics dv = a(b v4)dt + c/vdWt, Vo > 0, 1 where a, b, and c are
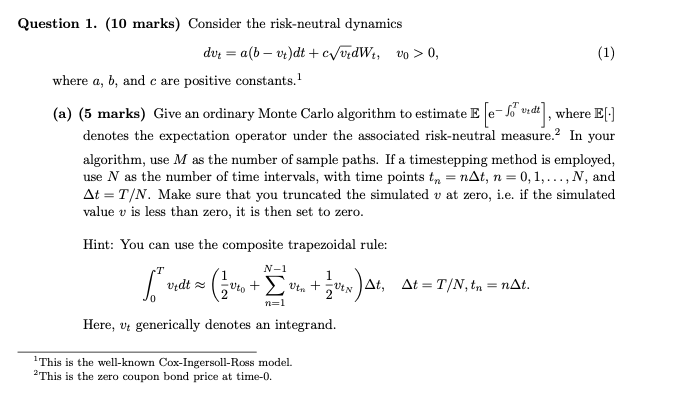

(1) Question 1. (10 marks) Consider the risk-neutral dynamics dv = a(b v4)dt + c/vdWt, Vo > 0, 1 where a, b, and c are positive constants.! (a) (5 marks) Give an ordinary Monte Carlo algorithm to estimate E e- 1 vedt), where E[1] denotes the expectation operator under the associated risk-neutral measure. In your algorithm, use M as the number of sample paths. If a timestepping method is employed, use N as the number of time intervals, with time points tn = nAt, n=0,1,..., N, and At =T/N. Make sure that you truncated the simulated v at zero, i.e. if the simulated value v is less than zero, it is then set to zero. Hint: You can use the composite trapezoidal rule: N-1 1 ( tel = (+ widt + v +vat, At=T/N, tn = nAt. va)at, n=1 Here, vt generically denotes an integrand. This is the well-known Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model. 2 This is the zero coupon bond price at time-0. (b) (5 marks) Implementation of the above algorithm. Use the following parameters a = 1.5, b = 0.06, C = 0.7, 00 = 0.1 and T = 0.5. Carry out experiments with sequences of (MN) {(M., N.), (2M., 2N),..., (16M, 16N.)} and report the Monte Carlo estimates, together with standard errors, and 95% confidence intervals. For this question, you are free to choose M, and N, sufficiently large. Typical values are Mo = 109 and No = 25. (1) Question 1. (10 marks) Consider the risk-neutral dynamics dv = a(b v4)dt + c/vdWt, Vo > 0, 1 where a, b, and c are positive constants.! (a) (5 marks) Give an ordinary Monte Carlo algorithm to estimate E e- 1 vedt), where E[1] denotes the expectation operator under the associated risk-neutral measure. In your algorithm, use M as the number of sample paths. If a timestepping method is employed, use N as the number of time intervals, with time points tn = nAt, n=0,1,..., N, and At =T/N. Make sure that you truncated the simulated v at zero, i.e. if the simulated value v is less than zero, it is then set to zero. Hint: You can use the composite trapezoidal rule: N-1 1 ( tel = (+ widt + v +vat, At=T/N, tn = nAt. va)at, n=1 Here, vt generically denotes an integrand. This is the well-known Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model. 2 This is the zero coupon bond price at time-0. (b) (5 marks) Implementation of the above algorithm. Use the following parameters a = 1.5, b = 0.06, C = 0.7, 00 = 0.1 and T = 0.5. Carry out experiments with sequences of (MN) {(M., N.), (2M., 2N),..., (16M, 16N.)} and report the Monte Carlo estimates, together with standard errors, and 95% confidence intervals. For this question, you are free to choose M, and N, sufficiently large. Typical values are Mo = 109 and No = 25
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


