Question: (1) Quicksort. In this question, we will analyze picking the pivot by taking 3 numbers from the array at random and then taking the median

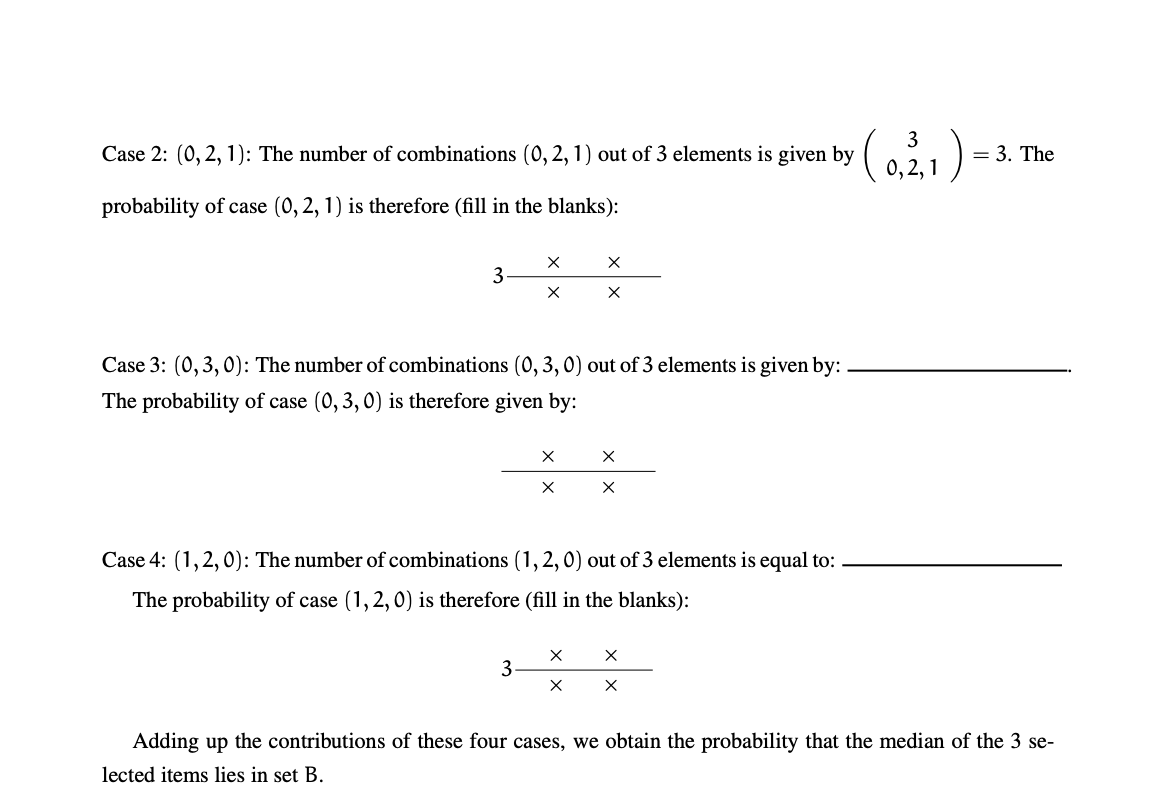
(1) Quicksort. In this question, we will analyze picking the pivot by taking 3 numbers from the array at random and then taking the median of these three. The question is the probability that this pivot is close to the real median of the array. Suppose we define three sets, A, B, and C. A consists of the a smallest numbers in the array to be sorted, C consists of the c largest numbers to be sorted and B is the rest of them: it has b = n-a-c numbers, where n is the length of the array to be sorted. Assume that min{a, b,c} > 3. Derive an expression for the probability that the middle of 3 elements randomly picked (without replace- ment) from the array is in set B. We started the process in class by looking at one of the cases; in this question, you will complete it. We'll need some notation for convenience. Denote by (i, j, k) the event that we select i items from A, j from B and k from C, all without replacement. The cases which lead to the median falling in set B are: (1,1,1),(0, 2, 1), (1,2,0), (0,3,0). We went over (1,1,1) in class. Follow these steps. (If you are reasonably familiar with probability, you can write down the answer directly, but if not, it helps to go through the steps one by one.) Case 1: (1,1,1). The probability that the first item to be picked out of the n is in set A is given by: a. The probability that the second item to be picked out of the n-1 remaining items is in set B is given by b The probability that the third item to be picked out of the n 2 remaining items is in set C is given by: The probability that the first second and third items are from sets A, B and C respectively is: The median will be in set B if any one of the three picks is from set A, any one from set B, and any 73 one from set C. The number of combinations (1,1,1) out of 3 elements is given by , ( 1,1,1) = -. (Look up multinomials online if you have forgotten what the preceding notation means.) So, the probability of the case (1,1,1) happening is given by: - 2 The Case 2: (0,2,1): The number of combinations (0, 2, 1) out of 3 elements is given by e viven by 1 3 (0,2,1 ) probability of case (0,2,1) is therefore (fill in the blanks): 3 X XX Case 3: (0,3,0): The number of combinations (0,3,0) out of 3 elements is given by: The probability of case (0,3,0) is therefore given by: XX XX Case 4: (1,2,0): The number of combinations (1,2,0) out of 3 elements is equal to: - The probability of case (1,2,0) is therefore (fill in the blanks): x x Adding up the contributions of these four cases, we obtain the probability that the median of the 3 se- lected items lies in set B. e d alumnes de e ntributions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


