Question: 1. Show the numerical computation of P(M|B,-E) using enumeration, where E stands for Earthquake, M for Mary Calls, B for Burglary, and -E stands for
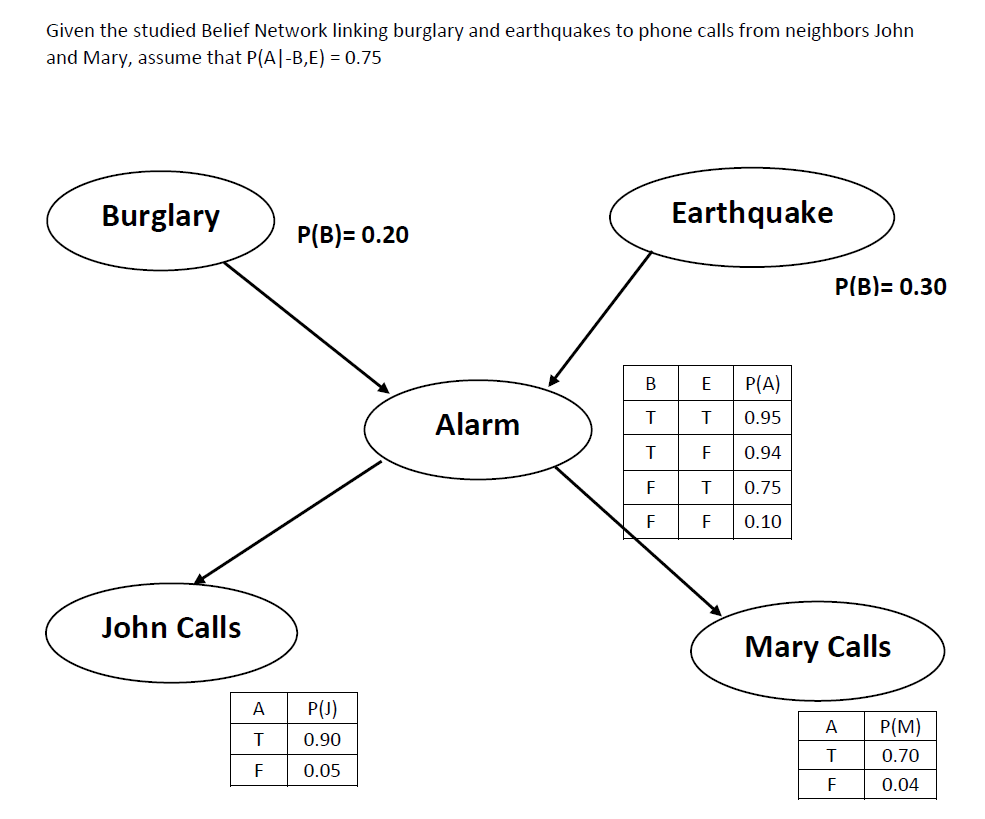
1. Show the numerical computation of P(M|B,-E) using enumeration, where E stands for Earthquake, M for Mary Calls, B for Burglary, and -E stands for 'Earthquake= False'. Also draw the call graph.
2. Show the numerical computation of P(M|B,-E) using variable elimination. Draw the call graph with values on arcs.
3. Generate samples based on the pseudo random number generator (PRNG) issuing the following sequence:
x0=0.75
xi=(xi-1 * 21 + 3)%100
Give the sequence of obtained numbers, relevant to your computation. A Boolean random variable X sampled at time i is generated as true, if (xi / 100 Given the studied Belief Network linking burglary and earthquakes to phone calls from neighbors John and Mary, assume that PIAI-8,E)-0.75 BurglaryP(B)- 0.20 Earthquake P(B) 0.30 B E P(A) T T 0.95 TF 0.94 F T 0.75 F F0.10 Alarm John Calls Mary Calls A P(U) T 0.90 F 0.05 A P(M) T 0.70 0.04 Given the studied Belief Network linking burglary and earthquakes to phone calls from neighbors John and Mary, assume that PIAI-8,E)-0.75 BurglaryP(B)- 0.20 Earthquake P(B) 0.30 B E P(A) T T 0.95 TF 0.94 F T 0.75 F F0.10 Alarm John Calls Mary Calls A P(U) T 0.90 F 0.05 A P(M) T 0.70 0.04
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


