Question: 1. Solve AT = b using Gaussian elimination without pivoting. Identify the matrices L, U such that LU = A. 12 co N b =
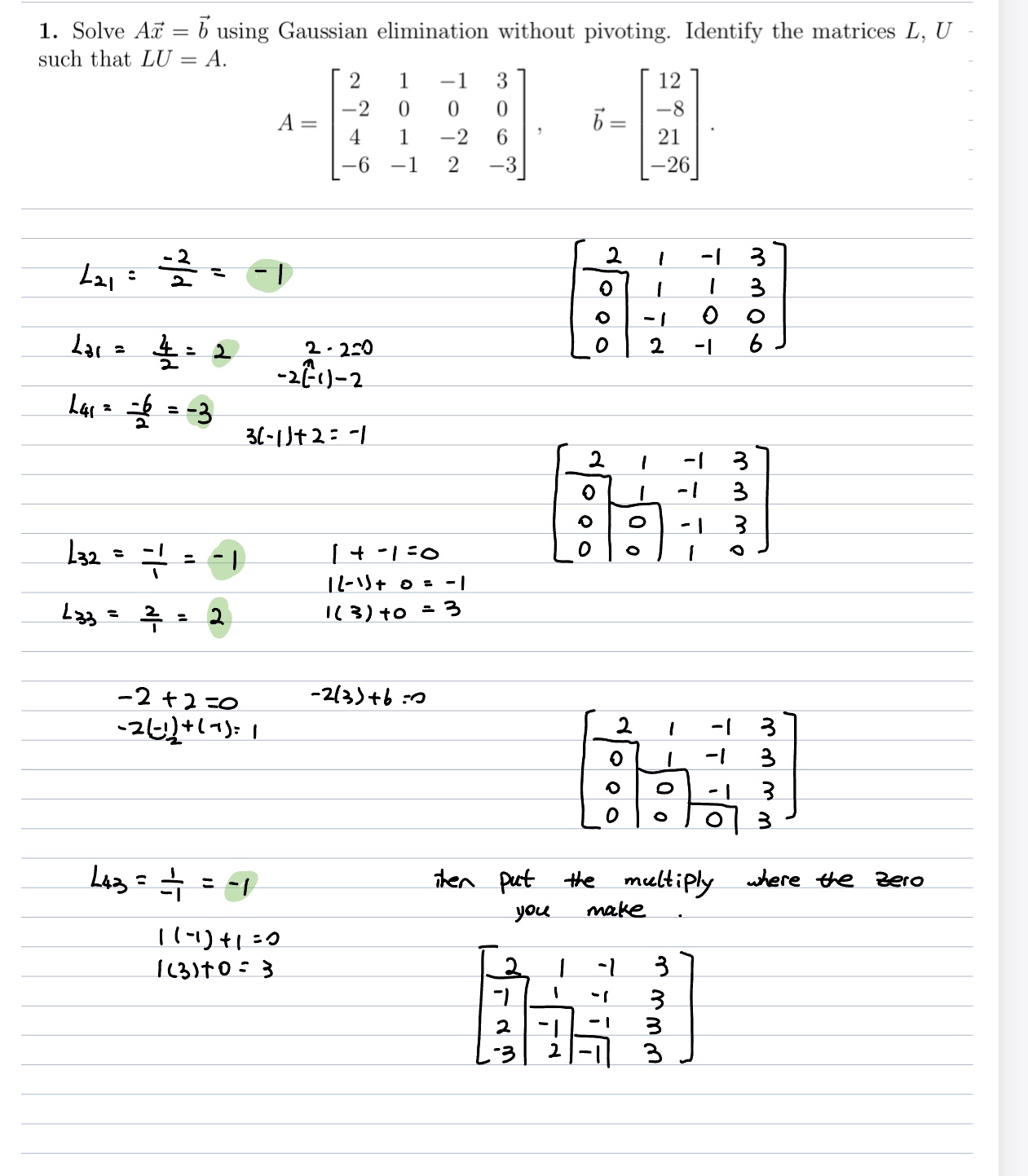



1. Solve AT = b using Gaussian elimination without pivoting. Identify the matrices L, U such that LU = A. 12 co N b = -8 A = 21 -6 2 26 2 I 3 221 : 2 = -1 - - ooo - Lar = 4 :2 2 - 250 -1 - 2 ( - 1) - 2 Lar z -6 =-3 3( - 1)+ 2 : -1 2 1 - 1 0 O W W - O 232 = = = - | 14 - 1=0 12-\\+ 0 = -1 Lag = 2 = 2 1( 3 ) to = 3 -2+2=0 -2(3) +6 :0 2 W - 2(-1) + (7): 1 0 w IN Oo w / then put the multiply where the zero you make 1 1 - 1 ) + 1 =0 1(3 ) to : 3 - 1 W\f\f1. Solve A = b using Gaussian elimination with partial pivoting. Identify the matrices L, U, P such that LU = PA. 2 L 12 -2 0 0 -8 A = b = 4 1 -2 21 6 2 3 26 2. Consider the same 4 x 4 matrix in Problem 1 above. 1. You computed the LU factorization for this matrix in Homework 1. Use this factor- ization, A = LU, to determine det( A). 2. Use the factorization from Problem 1, PA = LU, to determine det (A). 3. Describe how Gaussian elimination with partial pivoting can be used to find the de- terminant of a general square matrix
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


