Question: 1 Where is a processing the view where chave to As med mina va per The value of good pm Cosplorable valo AN 14. The
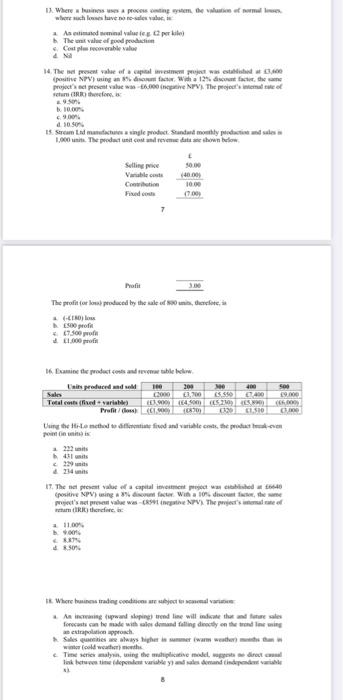
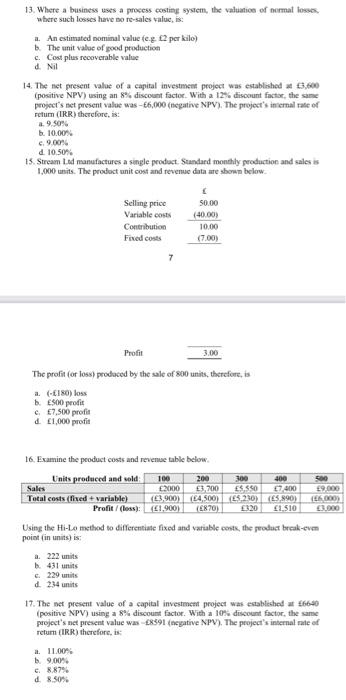


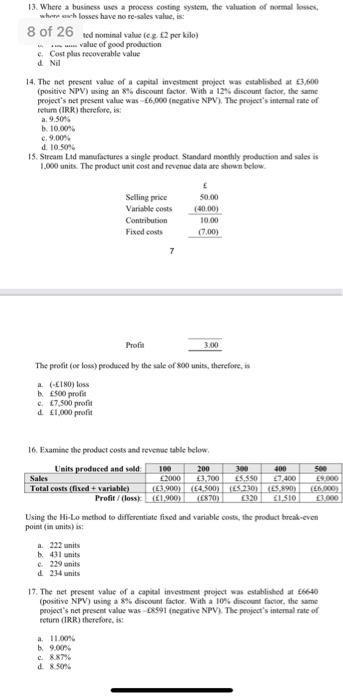
1 Where is a processing the view where chave to As med mina va per The value of good pm Cosplorable valo AN 14. The present vahe of met was established positie NPV) using and with a 12% discount factie theme project's et pecinta wachete NPV). The projet's temat of recher 2.950 10.00 9.00 100 15. Sercem ad manufacture single product Standardly production and des 1.800. The prodat net connevedown below Variables 2000 Cow 10.00 Find out 17.00) Mail 3. The profit for produced by the sale of me - ESO profie 7.500 Examine the products were Limits produced und MO Sales C2000,200 ES550 Total cost od variable 2004 som M 186.000 ProfiGow 000 Ung the file method Giftsfried and then the produce ponniain 233 i 229 24 is IT. The ne pret value of a capital invoient powalced to posite NPV) using rent factor WIB a 10 count theme t's et prevent al was create NPV The presence a Rity therefore, US it where hunam nadag on - As we upward sloping trendline will indicate that made sales forecasts can be made with a demand falling directly on the role in extrapon proch Salles que les away higher le summer warm weather (all meats the Time series in the plate modele direct cu link time dependent variable and independe 13. Where a business uses a process costing system, the valuation of normal losses where such losses have no re-sales value is 1. An estimated nominal value (eg 12 per kilo) The unit value of good production c. Cost plus recoverable value d. Nii 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established $3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor the same project's net present value was - 6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of retum (IRR) therefore, is 9.50% . 10.00% c. 9.00 d. 10.50% 15. Stream Led manufactures a single product Standard monthly production and sales is 1,000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below. Selling price Variable costs Contribution Fixed costs 7 50.00 (40.00) 10.00 Profil 3.00 The profit (or loss produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, is a. (180) loss b. ES00 prodit 7,500 profit d 1,000 profit 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below 500 Units produced and sold 100 200 300 400 Sales 2000 3,700 5.550 7400 9.000 Total costs (fixed variable) 3.900 (4,500)ES 230) (5.890) 16.000) Profit/(less): (41.900) (E870) 1.510 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-evm point in units) is a. 222 units 431 units 5. 229 units) d. 234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's net present value was 8391 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of retum (IRR) therefore, is a. 11.00% b. 9.00% d. 8.50% 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below. Units produced and sold: 100 200 300 400 500 Sales 2000 3,700 5,550 7,400 9,000 Total costs (fixed + variable) (3.900) (4,500) (5,230) (5.890) (6,000 Profit/ (loss): (E1.900) (870) 320 1,510 3,000 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-even point (in units) is: a. 222 units b. 431 units c. 229 units d. 234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's net present value was - 8591 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a 11.00% b. 9.00% c. 8.87% d. 8.50% 18. Where business trading conditions are subject to seasonal variation: a. An increasing (upward sloping) trend line will indicate that and future sales forecasts can be made with sales demand falling directly on the trend line using an extrapolation approach. b. Sales quantities are always higher in summer (warm weather) months than in winter (cold weather) months. c. Time series analysis, using the multiplicative model, suggests no direct causal link between time (dependent variable y) and sales demand (independent variable X). 8 d. Future sales demand (or other business factor) forecasting can be made using the trend line adjusted +/- for the calculated seasonal variation factor 13. Where a business uses a process costing system, the valuation of normal losses, where such losses have no re-sales value is: a. An estimated nominal value (e.g. 2 per kilo) b. The unit value of good production c. Cost plus recoverable value d. Nil 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor, the same project's net present value was - 6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a. 9.50% b. 10.00% c. 9.00% d. 10.50% 15. Stream Ltd manufactures a single product. Standard monthly production and sales is 1,000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below. Selling price 50.00 Variable costs (40.00) Contribution 10.00 Fixed costs (7.00) 7 Profit 3.00 The profit (or loss) produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, is a. (-180) loss b. 500 profit c. 7,500 profit d. 1,000 profit 13. Where a businesses a process costing system, the valuation of nemal Soses, no resales 8 of 26 ned nominal value les 2 per kilo) value of good production Cost plus recoverable value Nil 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor, the same project's tet present value was -6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is a 9.50 b. 10.00 9.00% d. 10.50% 15. Strcam Lad manufactures a single product Standard monthly production and sales is 1.000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below 50.00 (40.00) Selling price Variable costs Contribution Fixed costs 7 10.00 (7.00) Profil 3.00 The profit (or lows) produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, in (LINO) foss 500 profit 7,500 profit d1,000 profit 200 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below Units produced and sold 100 300 400 Sales E000 1,700 17.400 Total costs (fixed + variable) (3.900) (4,500) 5.230) (15,890) TEL 000 Profit (lossy (1 900) (E870) 320 1 310 000 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-even point in units) is 222 units b. 431 units . 229 units d234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's not present value was 08591 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a. 11.00% b. 9.00 c88796 d&sor 1 Where is a processing the view where chave to As med mina va per The value of good pm Cosplorable valo AN 14. The present vahe of met was established positie NPV) using and with a 12% discount factie theme project's et pecinta wachete NPV). The projet's temat of recher 2.950 10.00 9.00 100 15. Sercem ad manufacture single product Standardly production and des 1.800. The prodat net connevedown below Variables 2000 Cow 10.00 Find out 17.00) Mail 3. The profit for produced by the sale of me - ESO profie 7.500 Examine the products were Limits produced und MO Sales C2000,200 ES550 Total cost od variable 2004 som M 186.000 ProfiGow 000 Ung the file method Giftsfried and then the produce ponniain 233 i 229 24 is IT. The ne pret value of a capital invoient powalced to posite NPV) using rent factor WIB a 10 count theme t's et prevent al was create NPV The presence a Rity therefore, US it where hunam nadag on - As we upward sloping trendline will indicate that made sales forecasts can be made with a demand falling directly on the role in extrapon proch Salles que les away higher le summer warm weather (all meats the Time series in the plate modele direct cu link time dependent variable and independe 13. Where a business uses a process costing system, the valuation of normal losses where such losses have no re-sales value is 1. An estimated nominal value (eg 12 per kilo) The unit value of good production c. Cost plus recoverable value d. Nii 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established $3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor the same project's net present value was - 6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of retum (IRR) therefore, is 9.50% . 10.00% c. 9.00 d. 10.50% 15. Stream Led manufactures a single product Standard monthly production and sales is 1,000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below. Selling price Variable costs Contribution Fixed costs 7 50.00 (40.00) 10.00 Profil 3.00 The profit (or loss produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, is a. (180) loss b. ES00 prodit 7,500 profit d 1,000 profit 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below 500 Units produced and sold 100 200 300 400 Sales 2000 3,700 5.550 7400 9.000 Total costs (fixed variable) 3.900 (4,500)ES 230) (5.890) 16.000) Profit/(less): (41.900) (E870) 1.510 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-evm point in units) is a. 222 units 431 units 5. 229 units) d. 234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's net present value was 8391 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of retum (IRR) therefore, is a. 11.00% b. 9.00% d. 8.50% 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below. Units produced and sold: 100 200 300 400 500 Sales 2000 3,700 5,550 7,400 9,000 Total costs (fixed + variable) (3.900) (4,500) (5,230) (5.890) (6,000 Profit/ (loss): (E1.900) (870) 320 1,510 3,000 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-even point (in units) is: a. 222 units b. 431 units c. 229 units d. 234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's net present value was - 8591 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a 11.00% b. 9.00% c. 8.87% d. 8.50% 18. Where business trading conditions are subject to seasonal variation: a. An increasing (upward sloping) trend line will indicate that and future sales forecasts can be made with sales demand falling directly on the trend line using an extrapolation approach. b. Sales quantities are always higher in summer (warm weather) months than in winter (cold weather) months. c. Time series analysis, using the multiplicative model, suggests no direct causal link between time (dependent variable y) and sales demand (independent variable X). 8 d. Future sales demand (or other business factor) forecasting can be made using the trend line adjusted +/- for the calculated seasonal variation factor 13. Where a business uses a process costing system, the valuation of normal losses, where such losses have no re-sales value is: a. An estimated nominal value (e.g. 2 per kilo) b. The unit value of good production c. Cost plus recoverable value d. Nil 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor, the same project's net present value was - 6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a. 9.50% b. 10.00% c. 9.00% d. 10.50% 15. Stream Ltd manufactures a single product. Standard monthly production and sales is 1,000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below. Selling price 50.00 Variable costs (40.00) Contribution 10.00 Fixed costs (7.00) 7 Profit 3.00 The profit (or loss) produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, is a. (-180) loss b. 500 profit c. 7,500 profit d. 1,000 profit 13. Where a businesses a process costing system, the valuation of nemal Soses, no resales 8 of 26 ned nominal value les 2 per kilo) value of good production Cost plus recoverable value Nil 14. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 3,600 (positive NPV) using an 8% discount factor. With a 12% discount factor, the same project's tet present value was -6,000 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is a 9.50 b. 10.00 9.00% d. 10.50% 15. Strcam Lad manufactures a single product Standard monthly production and sales is 1.000 units. The product unit cost and revenue data are shown below 50.00 (40.00) Selling price Variable costs Contribution Fixed costs 7 10.00 (7.00) Profil 3.00 The profit (or lows) produced by the sale of 800 units, therefore, in (LINO) foss 500 profit 7,500 profit d1,000 profit 200 16. Examine the product costs and revenue table below Units produced and sold 100 300 400 Sales E000 1,700 17.400 Total costs (fixed + variable) (3.900) (4,500) 5.230) (15,890) TEL 000 Profit (lossy (1 900) (E870) 320 1 310 000 Using the Hi-Lo method to differentiate fixed and variable costs, the product break-even point in units) is 222 units b. 431 units . 229 units d234 units 17. The net present value of a capital investment project was established at 6640 (positive NPV) using a 8% discount factor. With a 10% discount factor, the same project's not present value was 08591 (negative NPV). The project's internal rate of return (IRR) therefore, is: a. 11.00% b. 9.00 c88796 d&sor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


