Question: 1. Which one is considered a core (operational) business process? A) Human Resource B) Information Systems C) Engineering D) Finance 2. Which one is less
1. Which one is considered a core (operational) business process? A) Human Resource B) Information Systems C) Engineering D) Finance
2. Which one is less likely a KPI for the sales department? A) profit margin B) sales growth C) average time for customer conversion D) achievement rate of sales target
3. Which of the following is NOT a potential conflict between the sales and operations departments? A) level of product variety B) inventory level C) accounts receivable days D) level of customization
4. Which of the following is not an input to the aggregate planning process? A) cost information B) demand forecast C) policies on workforce changes D) master production schedules
5. One option for altering the availability of manufacturing capacity is: A) pricing. B) promotion. C) backorders. D) inventories.
6. In using the chase strategy, variations in demand could be met by: A) stablizing output during the regular time without changing employment levels. B) varying output during regular time by changing employment levels. C) varying backorders. D) varying inventory levels.
Consider the following information: (for Questions 7 and 8) Period Forecast 1 200 2 250 3 400 4 500 5 300 6 150 Regular Time: $20 per unit (300 units per period maximum) Overtime: $30 per unit (200 units per period maximum) Hire/Layoff Cost: None Beginning Inventory: None Inventory carrying cost: $1 per unit per period Backorder Cost: $5 per unit per period
7. In using the level strategy with maximum regular capacity without overtime, what is the total cost (choose the range that fits your answer)? A) >$20,000 B) $20,000 to $30,000 C) $30,000 to $40,000 D) >$40,000
8. In using the chase strategy with both regular and overtime capacities, what is the total cost (choose the range that fits your answer)? A) >$20,000 B) $20,000 to $30,000 C) $30,000 to $40,000 D) >$40,000
Table 1
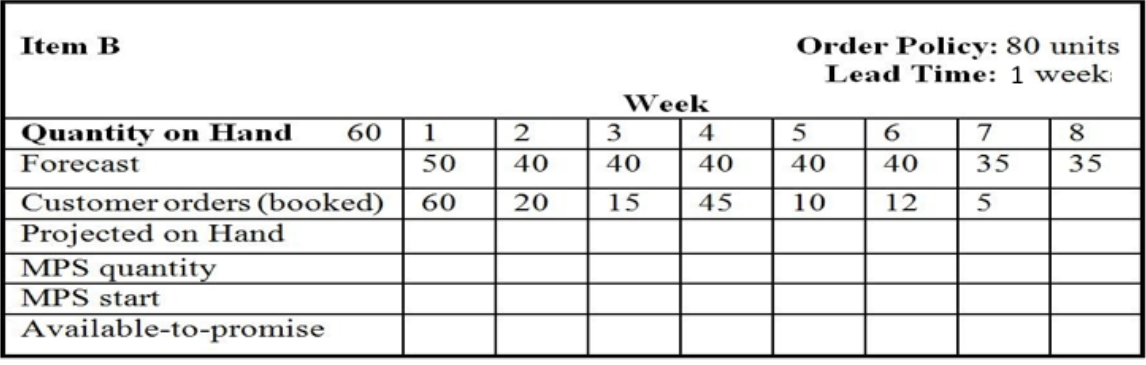 9. Use the information in partially completed Table 1. What is the projected on-hand inventory in week 5? A) 0 units B) 35 units C) 40 units D) 75 units
9. Use the information in partially completed Table 1. What is the projected on-hand inventory in week 5? A) 0 units B) 35 units C) 40 units D) 75 units
10. Use the information in partially completed Table 1. What is the MPS start quantity in week 2? A) 0 units B) 20 units C) 40 units D) 80 units
11. Use the information in partially completed Table 1. What is the available-to-promise (ATP) inventory in week 5? A) 0 units B) 35 units C) 53 units D) 80 units
12. Which one of the following is an input to the MRP system? A) shop-floor schedules B) financial reports C) master production schedule D) purchasing orders
Master Production Schedule: The following table shows the MPS start quantities for the next 10 weeks. Table 2 Finished Item A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 MPS start 20 40 30 20 40 Bill of Material: - Finished Goods A uses 2 each of component B, 1 each of component C. - Subassembly B uses 2 each of component D.
Selected Inventory Data: Table 3
| Item | Lot Sizing Rule | Lead Time | Scheduled Receipts | On-Hand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | L4L | 1 | 40 in period 1 | |
| C | FOQ = 50 | 2 | 40 | |
| D | POQ = 3 | 1 | 100 |
Construct the MRP schedule using the preceding information and answer the following questions.
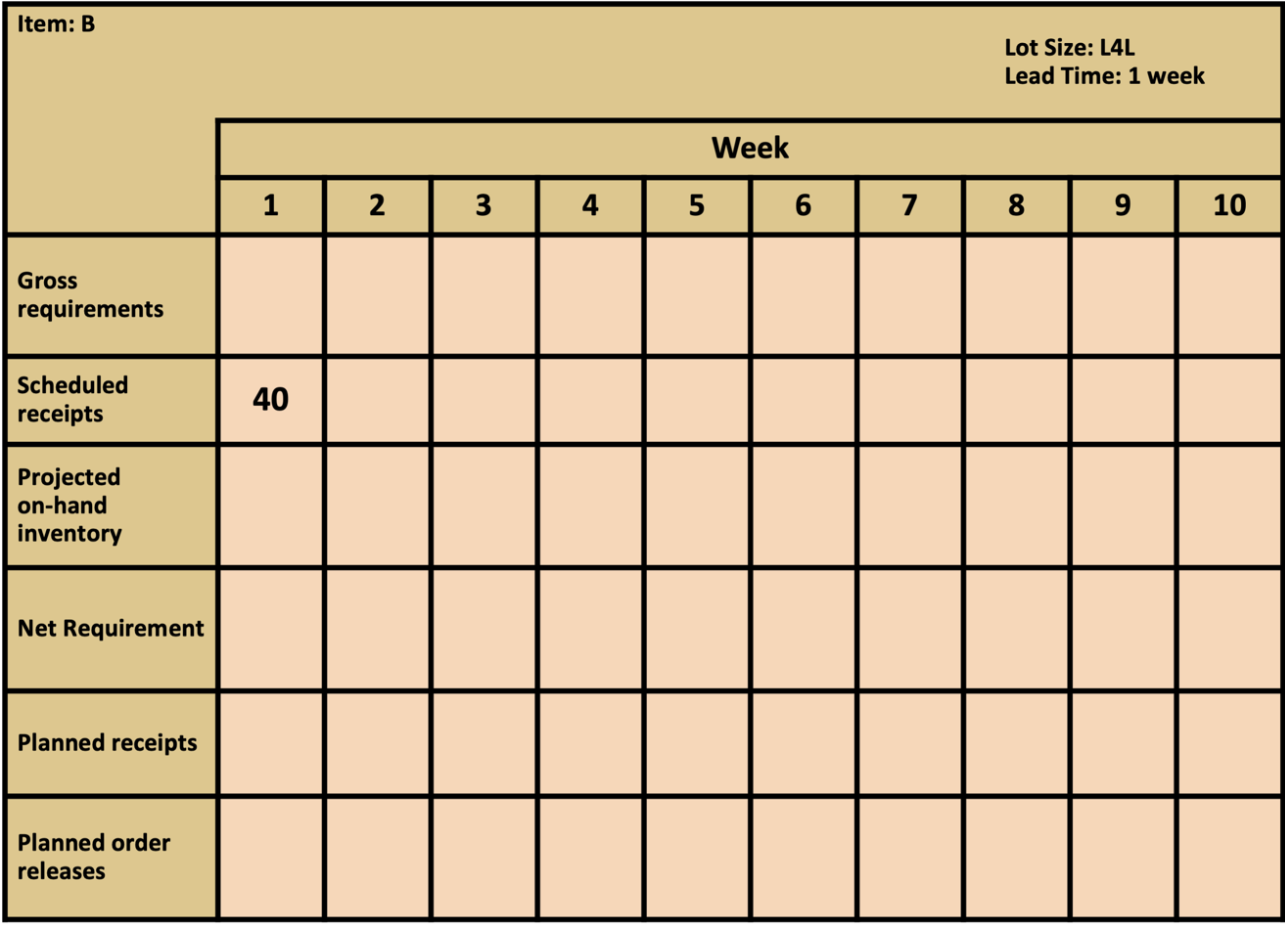
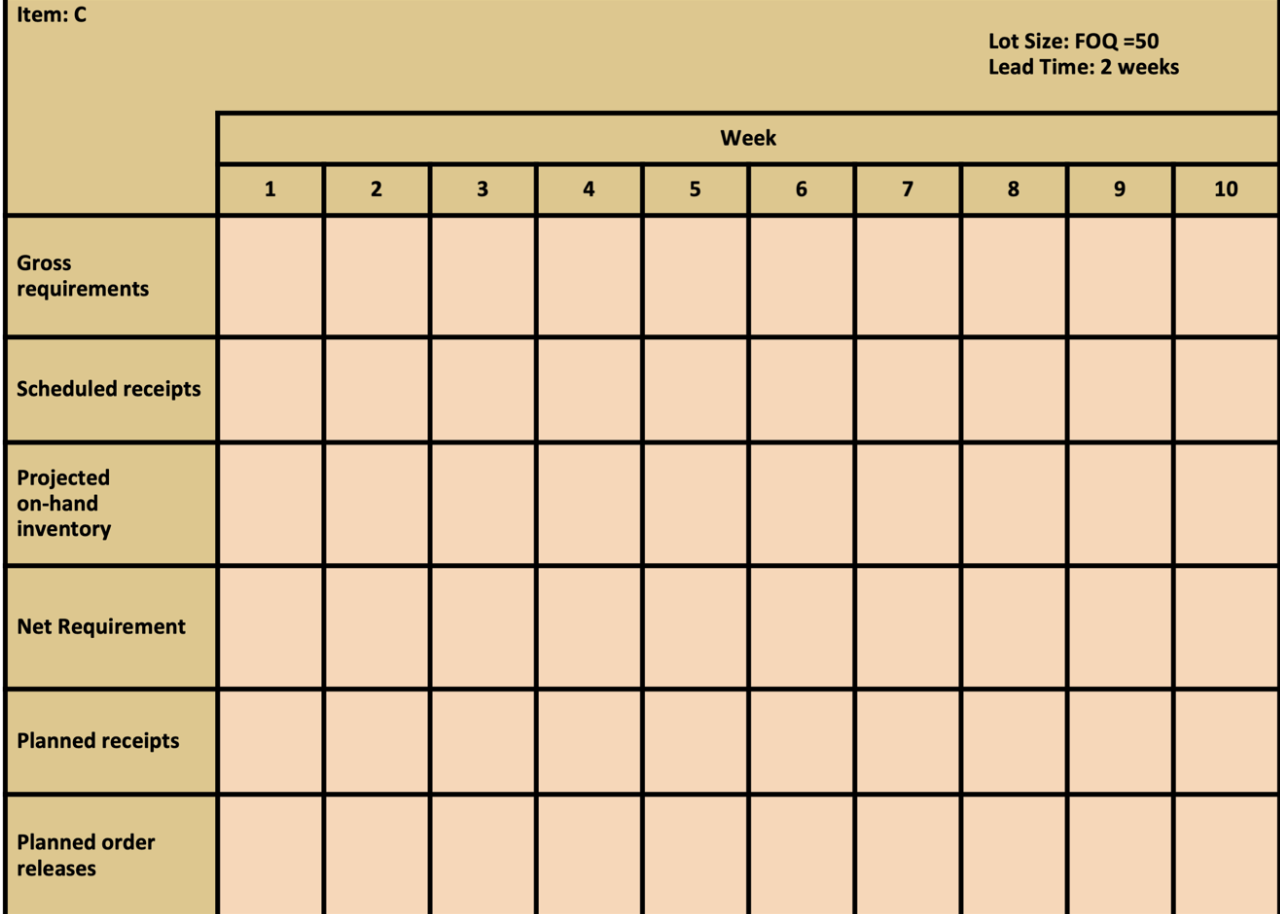
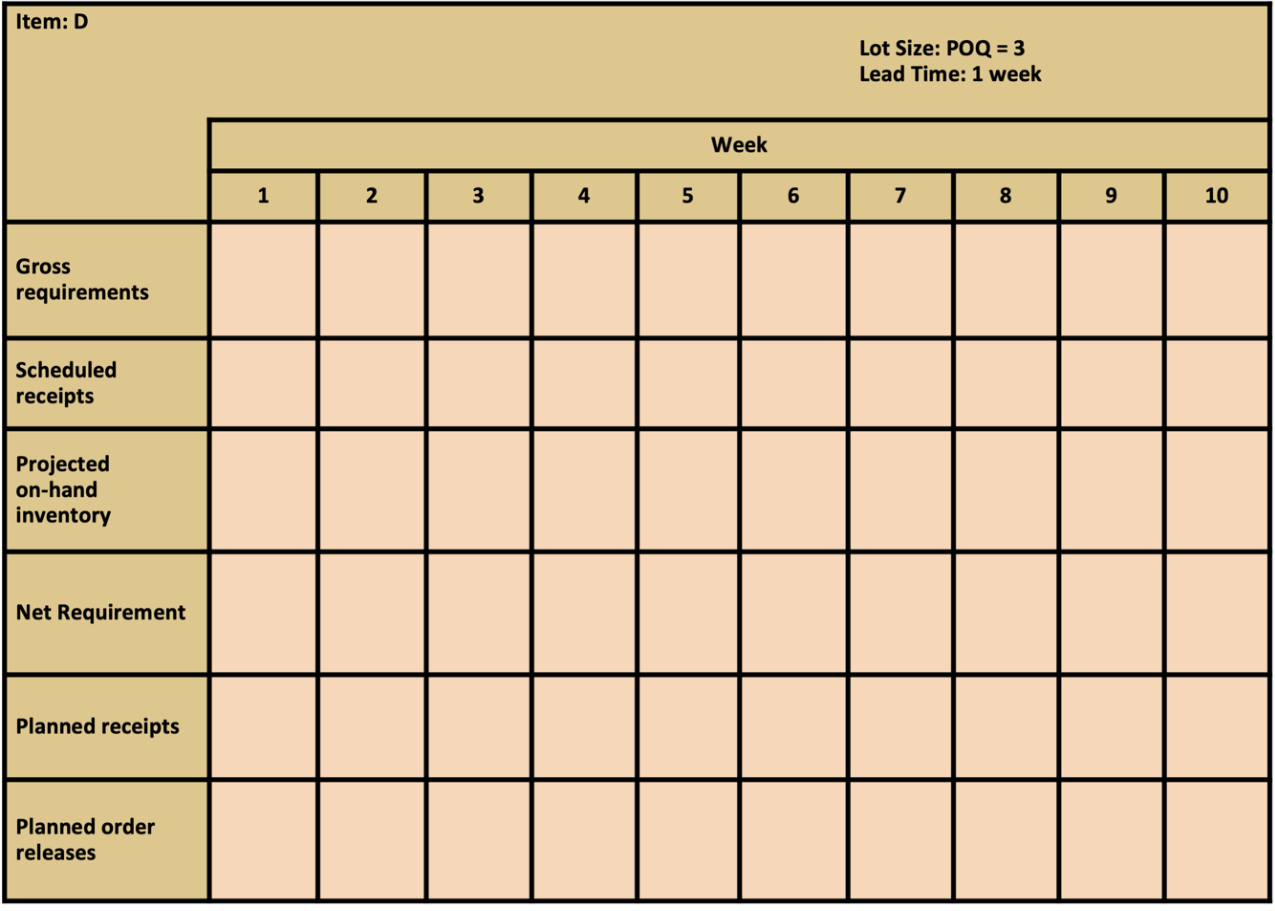
13. Use the information above. How many units of B are needed to produce 10 units of A? A) 10 units B) 20 units C) 30 units D) 40 units
14. Use the information above. What is the projected on-hand inventory for B in week 5? A) 0 units B) 35 units C) 40 units D) 75 units
15. Use the information above. How many planned order releases are there for item B? A) zero or one B) two C) three D) more than three
16. Use the information above. What is the projected on-hand inventory for C in week 6? A) 0 units B) 30 units C) 40 units D) 75 units
17. Use the information above. What is the gross requirement for D in week 2? A) 0 units B) 80 units C) 160 units D) 240 units
18. Use the information above. What is the projected on-hand inventory for D in week 5? A) 0 units B) 35 units C) 120 units D) 160 units
19. Which of the following statements concerning MRP systems (MRP I and MRP II) of the 1970s/80s is inaccurate? A) MRP systems are driven by a MPS and show the quantity and timing of end-item production B) Initial MRP-focused on material only, produced a schedule of shop order manufacturing dates (and purchase order release dates) C) MRP II scope was expanded to address machine and labor resources D) MRPII could optimize the profit and on-time performance subject to constraints
20. In many organizations, information flows much more freely within functions than it does across functions. __________ represents an expanded effort to overcome this tendency. A) MRP B) ERP C) CRP D) MRPII
Order Policy: 80 units Lead Time: 1 week: Item: B Lot Size: L4L Lead Time: 1 week Item: C Lot Size: FOQ=50 Lead Time: 2 weeks Item: D Lot Size: POQ=3 Lead Time: 1 week
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


