Question: 1. Write a program to generate a Huffman tree and corresponding message codes. Build a min-heap keyed with the frequencies. Run for the problem of

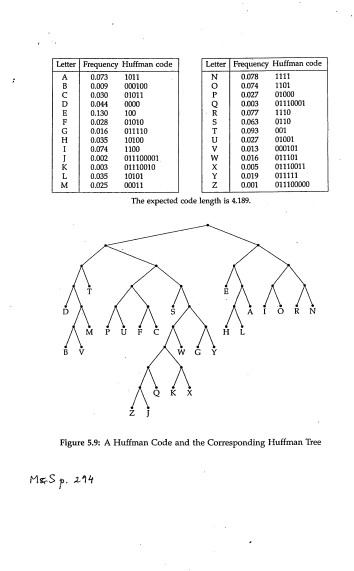
1. Write a program to generate a Huffman tree and corresponding message codes. Build a min-heap keyed with the frequencies. Run for the problem of Moret and Shapiro 294. Eigure 5.9 and for the Exercise #4 of Section 4.8 in Version 2 HSR (Huffman decode tree and codes for messages (M M7) with frequencies (q1..,q7) (4,5,7,8,10,12,20). Output the message code and the weighted average code word length for each frequency, as well as the total weighted external path length for the tree 2. Generate sets of n frequencies at random and run your program for increasing n. Time the execution of (1) building the initial heap keyed with the frequencies; and (2) the complete generation of the Huffman tree. Graph the times as a function of n. Notes: (a) To get more accurate results, you can repeat the Huffman tree construction a number of times and use the average time. (b) The size of the problem should not be limited by the use of static arrays (use dynamic memory allocation). Your report should include a comparison of the observed performance with the expected theoretical behavior. Note that the building of the heap should be done in linear time. 1. Write a program to generate a Huffman tree and corresponding message codes. Build a min-heap keyed with the frequencies. Run for the problem of Moret and Shapiro 294. Eigure 5.9 and for the Exercise #4 of Section 4.8 in Version 2 HSR (Huffman decode tree and codes for messages (M M7) with frequencies (q1..,q7) (4,5,7,8,10,12,20). Output the message code and the weighted average code word length for each frequency, as well as the total weighted external path length for the tree 2. Generate sets of n frequencies at random and run your program for increasing n. Time the execution of (1) building the initial heap keyed with the frequencies; and (2) the complete generation of the Huffman tree. Graph the times as a function of n. Notes: (a) To get more accurate results, you can repeat the Huffman tree construction a number of times and use the average time. (b) The size of the problem should not be limited by the use of static arrays (use dynamic memory allocation). Your report should include a comparison of the observed performance with the expected theoretical behavior. Note that the building of the heap should be done in linear time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


