Question: 10.1 General homogeneous boundary conditions Eigenvalue problem Find a real number A and a function u / 0 such that u + Au =0 with
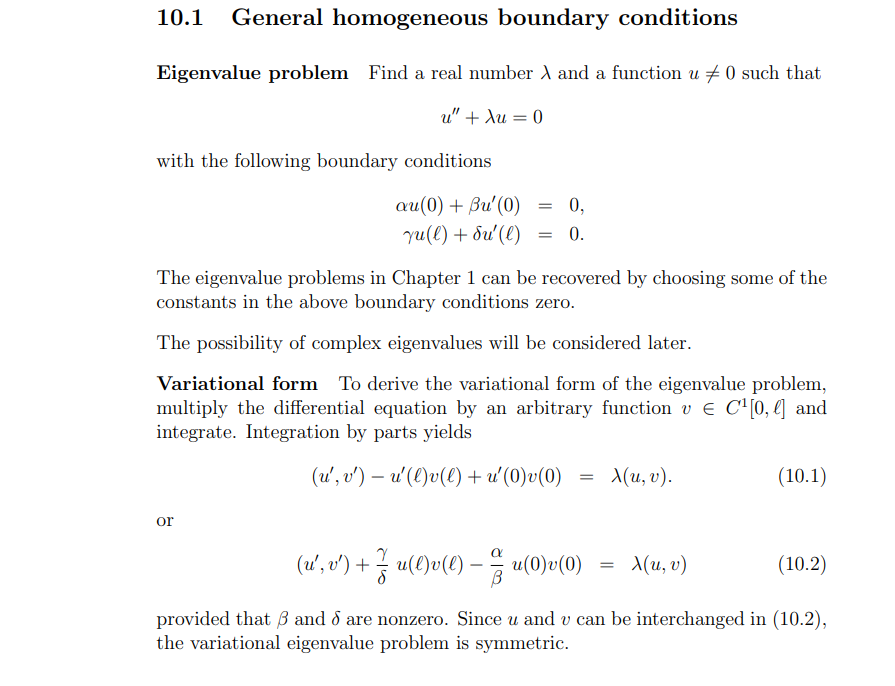

10.1 General homogeneous boundary conditions Eigenvalue problem Find a real number A and a function u / 0 such that u" + Au =0 with the following boundary conditions au(0) + Bu'(0) = 0, yu(e) + bu'(e) = 0. The eigenvalue problems in Chapter 1 can be recovered by choosing some of the constants in the above boundary conditions zero. The possibility of complex eigenvalues will be considered later. Variational form To derive the variational form of the eigenvalue problem, multiply the differential equation by an arbitrary function v e C'[0, (] and integrate. Integration by parts yields (u', v') - u'(e)v(l) + u'(0)v(0) = X(u, v). (10.1) or (u', v') + u(e)v(e) - - u(0)v(0) = X(u, v) (10.2) provided that S and o are nonzero. Since u and v can be interchanged in (10.2), the variational eigenvalue problem is symmetric.Special cases 1. If .6 = 6 = 0, we have the boundary conditions um) = ME) = U and we require that 11(0) = 3(6) = 0. It follows from {10.1) that (11'. L") = Mn: 1'). 2. If '5' = \"y = 0, we have the boundary conditions 3(0) = UTE) = U and we require that M0) = 0. Again, it follows from {10.1) that (11'. if) : Mn, 1!). 3. If (1 = q,- = (l, we have the boundary conditions 11303) = -u'() = I]. It follows that (1H,?!) = Mn: 11) from (10.1}. Orthogonality Suppose w is an eigenfunction with corresponding eigen value p: (of, L") + % u.r()v(f} :7: w(0)c(0} = Mm, v). Now, 1,- may be replaced by n in the equation above and 1; may be replaced by m in (10.2). Due to the symmetry of the left hand side of (10.2): it follows that Mmm} =Ju(t1.-'.Iu.). If A 3% p, then (any) =0. Eigenvalues If 76 2 U and a}? S 0._ then A 2 0. Exercises 10. 1 1. Calculate eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for the case or = .8 = 6 = 1 and q,- = 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


