Question: 12. A case study in the chapter analyzed purchasing-power parity for several countries using the price of Big Macs. Here are data for a few


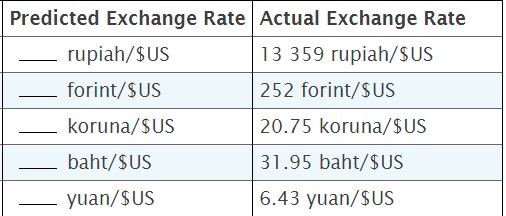
12. A case study in the chapter analyzed purchasing-power parity for several countries using the price of Big Macs. Here are data for a few more countries: Country Price of a Big Mac + Indonesia 35 750 rupiah Hungary 864 forint Czech Republic 79 koruna Thailand 119 baht China 20.4 yuan Source: Based on data from "The Big Mac Index," The Economist Newspaper Limited, London. January 17, 2018. https://www.economist.comews/2018/01/17/the-big-mac-index a. For each country, compute the predicted exchange rate of the local currency per U.S. dollar. (Recall that the U.S. price of a Big Mac was $5.28.) How well does the theory of purchasing-power parity explain exchange rates? b. According to purchasing-power parity, what is the predicted exchange rate between the Hungarian forint and the Chinese yuan? What is the actual exchange rate?Country Price of a Big Mac Predicted Exchange Rate Indonesia 35 750 rupiah rupiah/$ US Hungary 864 forint forint/$US Czech Republic 79 koruna koruna/$US Thailand 119 baht baht/SUS China 20.4 yuan yuan/$USPredicted Exchange Rate | Actual Exchange Rate rupiah/$US 13 359 rupiah/SUS forint/$US 252 forint/SUS koruna/$US 20.75 koruna/$US baht/SUS 31.95 baht/$US yuan/$US 6.43 yuan/$US
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


